IN THIS ARTICLE
Table of Contents
Hard work, patience, skill, determination, and the right allies bring about business success. Yes, you need partners to help you address your needs and realize your goals.
Among the partners you can collaborate with are business process outsourcing (BPO) companies. They can improve your organization’s value, performance, productivity, and revenue when you outsource some of your operations.
Decision-makers know that success is hard to attain through efforts alone. That is why outsourcing is a business strategy used by companies of all sizes and types.
This extensive yet easy guide covers what BPO is and everything you need to know about it.
What Is BPO?
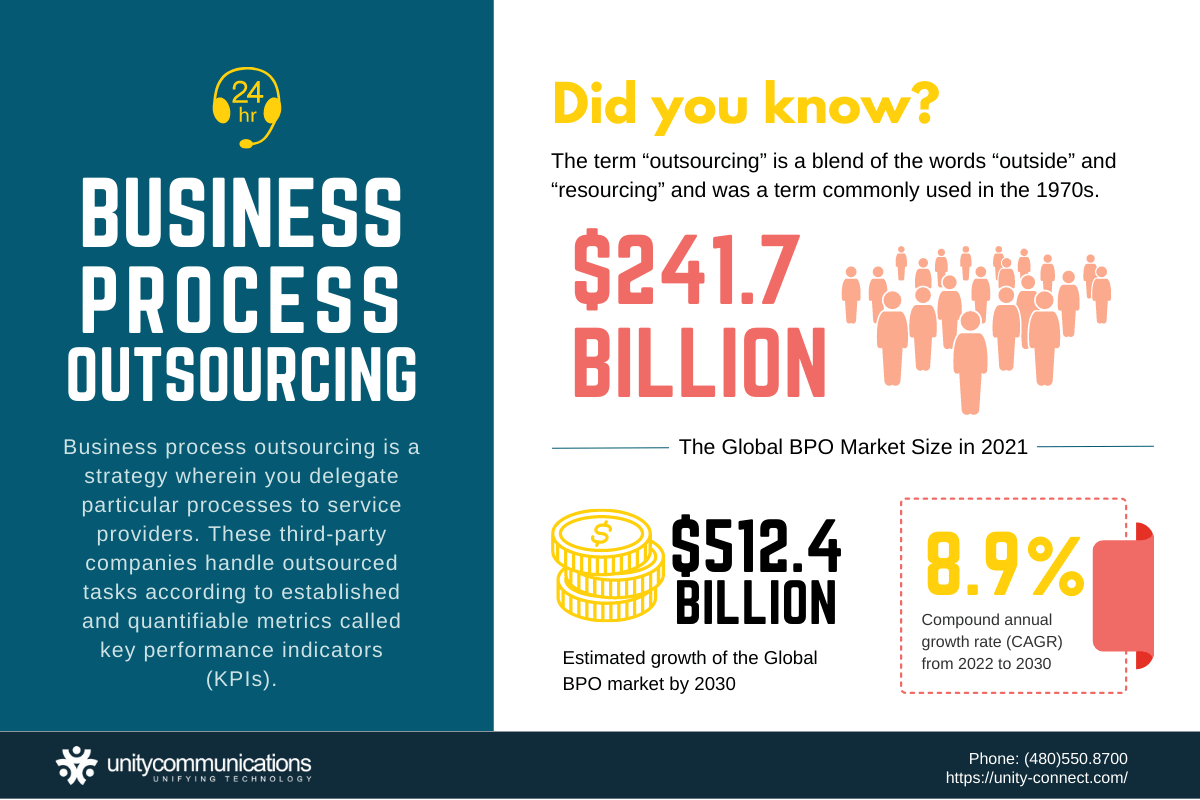
The acronym stands for “business process outsourcing” (BPO). It is a strategy wherein you delegate particular processes to service providers, also known as BPO providers. These third-party companies handle outsourced tasks according to established and quantifiable metrics called key performance indicators (KPIs).
The term “outsourcing” is a blend of the words “outside” and “resourcing” and was a term commonly used in the 1970s. It was a popular business strategy among manufacturers of soft drinks, automobiles, athletic shoes, and consumer products.
What Is the History of BPO?
The roots of Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) can be traced back to the 19th century, with its origins in bustling cities like New York and London. Back then, it was referred to as “subcontracting,” a strategy frequently employed by local merchants to have their goods produced by cost-effective external labor. Among the products that were commonly subcontracted included footwear, artificial flowers, brushes, scientific instruments, cigars, furniture, clocks, and clothing.
As we fast forward to the 20th century, the practice of outsourcing expanded its horizons. In the late 1980s, notably in the United States, major manufacturers recognized the benefits of reduced expenses in global shipping, transportation, freight, and telecommunications. This led them to relocate their production operations to emerging economies where skilled labor was available at a fraction of the cost.
Later, advancements in the realm of manufacturing data collection and analysis enabled businesses to more accurately monitor the efficacy of outsourced production operations remotely. Helping to ensure consistent productivity across global business processes.
The actual term “BPO” was coined by IBM in the 1990s when the tech giant outsourced its data entry processes to an independent service provider located in Asia.
Over the following decade, the BPO sector experienced significant growth, thanks in part to the widespread availability of the internet and the surge in global e-commerce. This era marked a period of unlimited long-distance communication, high-speed connectivity, and affordable cross-border business transactions.
What’s the BPO Industry’s Status From 2000 to 2021?
In the next two decades, the global BPO industry grew by leaps and bounds, reaching $92.5 billion in value in 2019. Aside from manufacturing, outsourcing expanded to other activities, including technical support, customer service, and sales.
The Americas, comprising the U.S. and Canada, grabbed the lion’s market share. Asia Pacific, Africa, the Middle East, and Europe trailed behind.
According to a report from Global Industry Analysts, the worldwide BPO market in 2020 peaked at almost $162 billion at the onset of the pandemic, when numerous lockdowns and social distancing protocols initially took effect.
Despite the global health crisis, the market kept growing, hitting $261.9 billion in 2022, based on a Grand View Research report.
What Is the BPO Industry’s Outlook From 2023 Onwards?
Bloomberg reports that the worldwide BPO market will maintain growth momentum in the next nine years. It will likely reach a market value of $620 billion by 2032 at an 8.5% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) within ten years.
North America will continue to corner a considerable share of the outsourcing business by region. The region will account for 60%, while Europe places second with 25% of the global BPO market pie.
Bloomberg cites two primary growth factors. The increasing adoption of robotic process automation (RPA) is the first growth factor. This artificial-intelligence-powered technology will assist human employees in tedious and repetitive tasks. The second growth factor is the move to a shared workload culture from centralized business strategies. The shift will achieve better results and profitability.
Regarding end users, the information technology (IT) and telecom sectors will grab more than 57% of the total outsourcing market value. The need for greater transparency and stricter regulations will drive BPO companies to standardize and streamline their operations.
Bloomberg also notes that BPO companies stand to gain from the normalization of remote work arrangements. Bigger organizations will depend on work-from-home (WFH) setups and will be open to recruiting the most qualified staff from across the nation or the world. The pandemic has paved the way and opened borders for BPO providers.
What Are the Types of BPO?
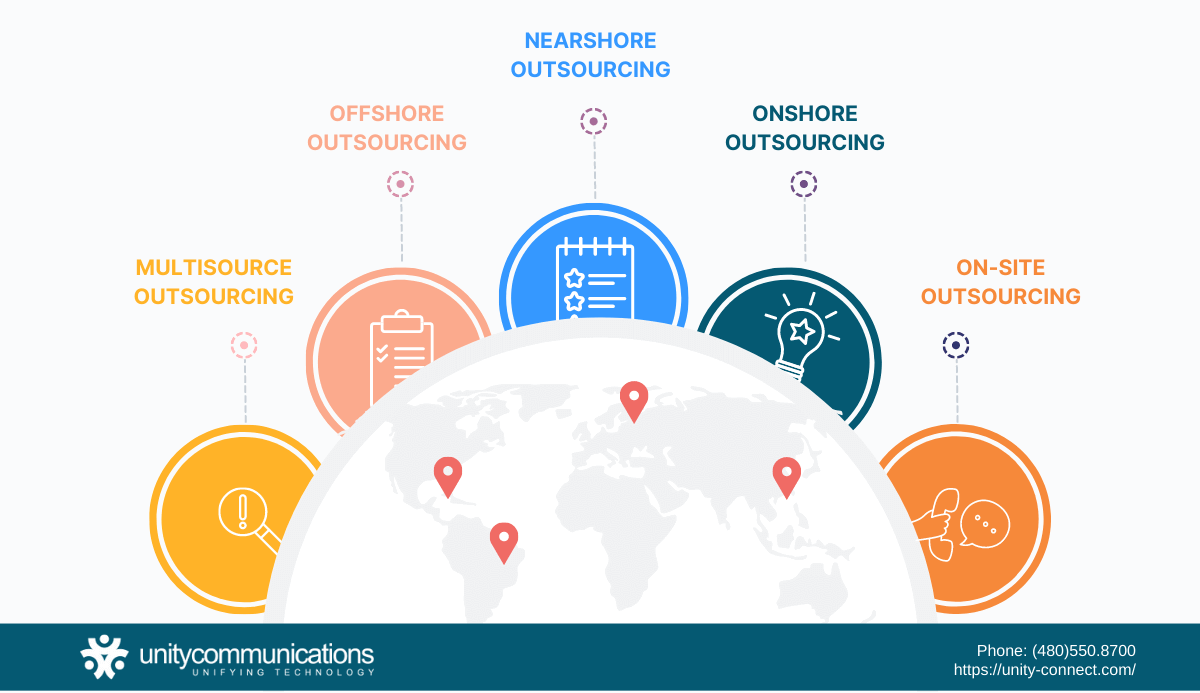
There are five types of BPO according to the third-party provider’s location. Choosing a type of outsourcing depends on your business requirements and goals. Let’s take a look at the five types of outsourcing:
- Multisource outsourcing is when you hire service providers from varying locations. This category combines the benefits of the different types of outsourcing. One main advantage is risk mitigation by delegating processes to several BPO providers rather than having them all in a single hub.
- Offshore outsourcing involves partnering with a BPO provider in another continent for your back-end processes. Cost-effective services are its greatest perk. The provider can offer more reasonable service rates since it employs a skilled and affordable workforce.
- Nearshore outsourcing means delegating processes to a third-party provider headquartered in a neighboring country. For example, your headquarters is in the U.S., while the service provider is in Puerto Rico. This approach offers faster communication than the other types of outsourcing.
- Onshore outsourcing is also known as local outsourcing. This type entails assigning jobs to a local BPO company. Your headquarters and that of your BPO partner are in the same country. Time zone and cultural differences are minimal concerns in this arrangement.
- On-site outsourcing involves a third-party provider dispatching workers to your company for specific tasks. Third-party professionals take responsibility for a certain period under the approved conditions. Hiring these workers as regular employees in the future is possible when opting for this strategic outsourcing method.
What Are Common BPO Services?

A BPO company offers two sets of processes: back-office services and front-office services.
1. Back-office Services
Also called internal business functions, back-office services include administrative or non-customer-facing activities. These functions support the front office and ensure everything runs smoothly in the background. The following are a few commonly outsourced back-office processes:
- Bookkeeping and accounting. Preparing financial documents and recording entries in ledgers or journals are some tasks you can delegate to a BPO provider. The third-party company supplies accounting workers and specialists ready to take on regular bookkeeping and accounting tasks such as auditing and compliance.
- Data entry. Encoding large amounts of data into computers and other digital devices with database or documentation software is another function contracted out to BPO vendors. These repetitive, detail-oriented, time-consuming tasks require manual skills and the latest technology.
- Technical support. Otherwise known as IT support, this is a crucial business segment involving various parts of outsourcing. The IT support team addresses customer and user questions, concerns, issues, or complaints regarding your services and products.
- Human resources (HR). The service provider handles the recruitment and hiring processes, onboards and trains employees, improves staff satisfaction and morale, and minimizes attrition. It helps your business processes by setting efficient HR systems, procedures, and workflow.
2. Front-office Services
These activities pertain to your customer-facing operations. Third-party team members assume the roles of customer service representatives (CSRs) for customers or clients. They are responsible for producing sales and revenue, providing a positive customer experience, and promoting or selling your products and services to the target market.
Here are the popular outsourced services:
- Customer support. This service involves directly interacting with customers to resolve problems, close sales, reply to questions and gather reviews or feedback. Support representatives are responsible for delivering excellent customer service to satisfy buyers or end users. They aim to retain consumer loyalty and increase repeat sales.
- Appointment setting. This function involves cold-calling clients and prospects to aid your sales team in meeting and speaking with them. The service provider has a team of specialists who engage with inbound and outbound client calls and hand potential customers over to your salespeople.
What Are BPO Subgroups?
BPO companies have evolved and diversified their services to meet client requirements and market demands. Initially serving the automotive and manufacturing sectors, the outsourcing business has broadened its network to cater to healthcare, e-commerce, retail, and banking.
This service expansion gave birth to the following subgroups:
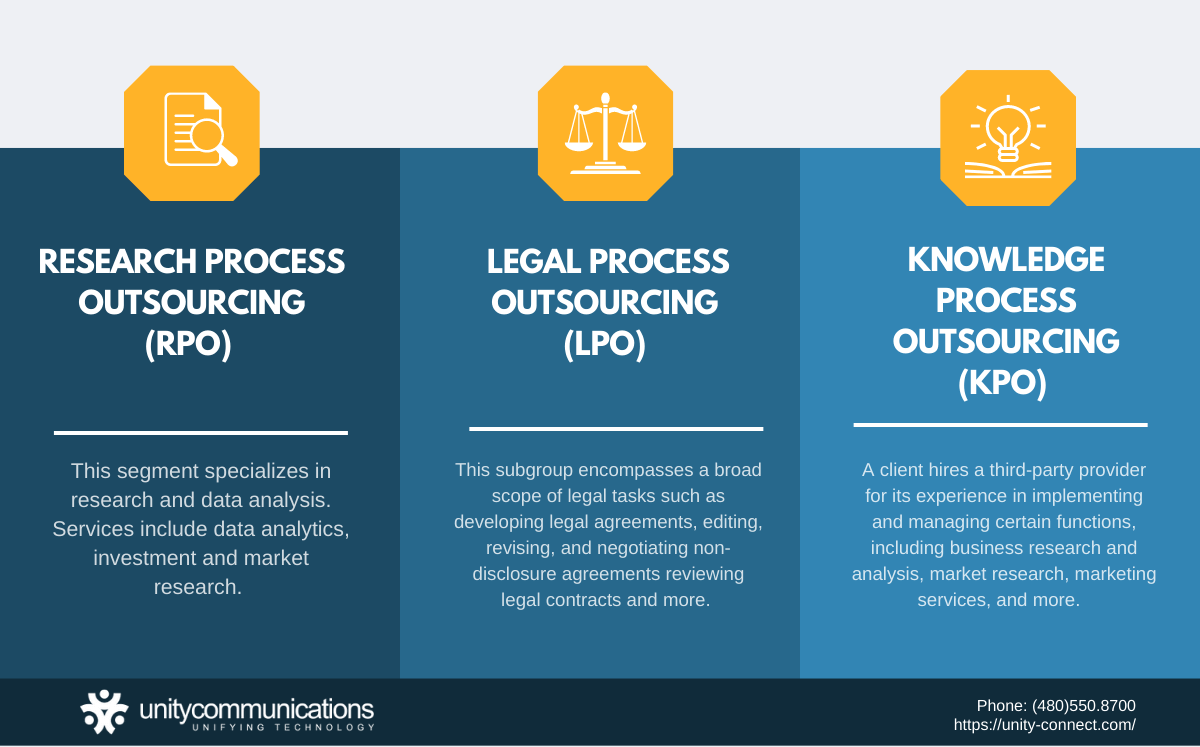
Research Process Outsourcing (RPO)
This segment specializes in research and data analysis. Data-dependent organizations, such as marketing agencies, biotech firms, investment companies, and pharmaceutical corporations, depend on this service. RPO services include:
- Data analytics
- Investment research
- Market research
Legal Process Outsourcing (LPO)
This subgroup encompasses a broad scope of legal tasks. These include a BPO company providing professional legal opinions and advice. Legal departments, law firms, and self-employed lawyers need LPO providers for different activities, such as:
- Developing legal agreements
- Editing, revising, and negotiating non-disclosure agreements
- Generating and preparing patent applications
- Performing legal research and analysis
- Reviewing legal contracts
LPO providers also offer clients a variety of specialists to support their legal processes, including:
- Billing clerks
- Case managers
- Compliance specialists
- Contract administrators
- Document coders
- Document processing specialists
- Paralegals
- Legal researchers
- Legal secretaries
Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)
A client hires a third-party provider for its experience implementing and managing certain functions. It recruits the provider to acquire expertise and extensive knowledge of processes. These specialized activities that KPO service providers handle include:
- Accounting
- Business research and analysis
- Content creation
- Design and animation
- Engineering service
- Financial research and analysis
- Market research
- Marketing services
- Publishing
- Web design
What Is BPO Catering To?

BPO is a growing business strategy on which the following industries rely:
- Telecommunications. Call center companies manage customer service and tech support for telecom providers (e.g., internet service, land and wireless communications, satellite, and cable providers). BPO companies provide customer support services, from receiving calls to convincing users to subscribe again.
- Software. Established and startup IT and software companies assign manufacturing operations overseas to obtain sufficient technical workers. Google, Microsoft, and Apple offshore their electronics consumer and technology products to Asian countries. The finished products are then sold to international markets.
- Retail products. E-commerce operators and online retailers delegate their retail-related tasks to third-party teams. These teams conduct transactions, take orders, handle purchases, and manage payment processing. Online businesses use the service providers’ multichannel, data capture, digital mailroom, and freight capabilities.
- Healthcare providers. Organizations hire BPO firms for medical coding, billing, data entry, and claims processing for maximum healthcare efficiency. Contractors gather relevant information and data for their healthcare and insurance clients. These clients also outsource tech support, customer service, and software development.
- Financial services. Banks, credit card companies, insurance firms, investment corporations, and other financial institutions depend on BPO services. Third-party teams collect payments on behalf of clients, reply to customer requests or questions, address financial issues, and fix or renegotiate overdue bills or accounts.
Who Are the Leading BPO Providers in the Outsourcing Market?
Below are the top BPO providers with ratings. The information is from Clutch, a business-to-business (B2B) rating website that lists companies in 500 industries in over 100 countries.
- Unity Communications (Rating: 4.9 Stars). Headquartered in Arizona, Unity Communications provides teams to help companies in the U.S., Canada, the UK, Australia, and Europe augment their staff.
- Helpware (Rating: 4.8 Stars). Helpware offers customized teams for customer support and back-office operations. Its services include data annotation, content moderation, data entry, and labeling.
- Conectys (Rating: 4.8 Stars). Based in Romania, Conectys delivers digital-first customer experience and content moderation services. It has multilingual teams in over 35 languages.
- LEX Reception (Rating: 4.9 Stars). This Oregon-based firm offers phone-based and round-the-clock receptionist, chat, legal answering, payment collection, and outbound calling services.
- Uassist.ME (Rating: 4.7 Stars). Headquartered in Florida, Uassist.ME provides outsourced business and virtual assistance services to small and midsize enterprises (SMEs), mostly in Latin America.
How BPO Helps Companies: Case Studies

The following are two outsourcing case studies demonstrating the effectiveness of this approach:
AT&T: Outsourced Services Exceeding Expectations
Challenge: AT&T was at a stage where they had to decide whether to maintain in-house call center operations.
Many representatives view customer service and similar roles as springboards to other careers. As such, the telecommunications provider saw that costs would rise if they sustained the workforce and maintained buildings and services. Morale would also drop.
Solution: AT&T’s leadership partnered with multiple vendors to build call centers for their business segments. The company tapped Unity Communications to work on the partner side, the Alliance Channel. This channel is focused on business customers, accounting for 20% of the total AT&T sales volume.
Result and benefits: In less than 12 months, Unity Communications helped improve AT&T’s wireless market share in Arizona by 4%. The BPO provider also enhanced AT&T’s competitive advantage, securing 15% of the domestic market. Since then, the service provider has launched campaigns in seven more AT&T markets.
Wireless Watchdogs: Achieving Growth Targets via Outsourcing
Challenge: Wireless Watchdogs is an industry leader in wireless management services. The company needed help when its help desk and tech support teams dwindled, forcing the remaining employees to work overtime. The lack of back-end support prevented its business operations from growing and its salespeople from closing deals.
Solution: The company partnered with Unity Communications, which developed a custom service-level agreement (SLA). The SLA includes KPIs to monitor task efficiency and success with the in-house team and a newly formed offline 24/7 team.
The BPO provider moved repetitive and time-consuming tasks to the offline team. Its agents then trained a team of four to five sales representatives on the tasks measured by metrics, such as priority, accuracy, and time to complete.
Results and benefits: Unity Communications’s offline team freed up Wireless Watchdogs’s top-paid employees’ time. It helped the wireless management company’s team exceed its SLA goals in only four months. This effort enabled sales representatives and customer-facing staff to reach their growth targets. Overtime was also eliminated, thus reducing payroll costs.
What Are the Advantages of BPO?
You should know the benefits of outsourcing when including BPO in long-term planning strategies. Check out the following advantages:
- Core competencies. Hiring a third-party team to handle the business’ non-core activities allows you to direct your resources to profitable ventures, including product or service innovation, marketing efforts, and research and development. Outsourcing can help you focus more on your core business functions to gain a competitive advantage.
- Decrease in total expenses. Outsourcing turns fixed costs into variable expenses. This means lower overhead costs and capital spending, saving you considerable money. You can then use the excess funds for other business activities.
- Efficiency at higher levels. Letting a third-party team help with processes can minimize delays, irregularities, inaccuracies, and waste. Enhanced efficiency and output mean greater customer service and better product or service quality.
- Hiring cost reduction. Looking for the right personnel, screening and interviewing candidates, and recruiting and training employees are expensive. You spend more time, effort, and money on these processes. A BPO provider can handle these tasks, finding and hiring competent people to fill the needed positions.
- Scalability, adaptability, and flexibility. A third-party provider can field the number of specialists necessary for outsourced tasks. It can adjust the staff size without interrupting operations. When it is time to reduce business operations, the provider can scale the team size down to help you save on costs.
What Are the Disadvantages of BPO?
Knowing the benefits and disadvantages of BPO enables you to perform a cost-benefit analysis of outsourcing. Below are its potential drawbacks:
- Inadequate knowledge. Your in-house team probably knows more about the company’s business, products, and services than the third-party team. While an in-house team is costlier due to high salaries, it is well-versed in your business. Assigning tasks to others with insufficient experience might affect your reputation and brand.
- Lack of administrative control. Outsourcing to a BPO provider means losing control over the delegated operations. The third-party provider uses proven and familiar measures, policies, and methods to manage outsourced activities. It might relegate or minimally use your procedures.
- Multiple duties. Some BPO companies have one team servicing two or more clients simultaneously, with or without your approval. This arrangement causes team members to allocate their skills, time, and valuable resources among clients to handle all the assigned tasks. Such a setup might result in below-average service quality.
- Shared confidential files. Sharing personal, critical, or sensitive information with a third-party provider is unavoidable when outsourcing processes such as tech support, bookkeeping and accounting, and customer service. Passwords, usernames, credit card numbers, and similar private accounts might be at risk of exposure.
- Undisclosed service fees. Some BPO providers make you incur hidden fees, undisclosed rates, and unexpected costs. It might submit client invoices for unforeseen incidents such as sudden and prolonged work disruptions (e.g., the pandemic) or employee termination.
What Are the Risks and Challenges Experienced by BPO Providers?

Like any business strategy, every outsourced work comes with risks. BPO providers face challenges regardless of their location, experience, and size. Let us look at five common challenges:
- Dealing with staff attrition and health concerns. Employee turnover in the BPO industry is higher than in other sectors. Finding and training new hires are expensive. Many third-party providers operate in countries with different time zones. This could result in health issues, particularly among agents in the graveyard or late-night shifts.
- Lacking qualified workers. The demand for outsourced services has grown as the BPO industry diversifies. It exceeds the supply of available skilled and competent talent. Many BPO firms struggle to obtain sufficient labor to fill the required positions.
- Managing intermittent disruptions. Poor internet connections, internal IT system malfunctions, unclear phone lines, and electric power interruptions are some setbacks affecting a service provider’s regular operations. Customers and clients expect providers to be accessible anytime. Disruptions lead to financial losses and complaints.
- Shifting economic and political conditions. Many BPO companies operate in regions with uncertain economic, social, and political stability (e.g., Asia Pacific, Eastern Europe, Central America, and Africa). Public unrest, economic downturns, and wars are some elements that can prevent providers from sustaining their operations.
- Surpassing high demands from clients. Many perceive tapping into the services of BPO companies as a cost-saving approach. As a result, market players feel pressured to provide the best possible service for clients while operating within a limited budget. Tightening market competition is one of the reasons this situation persists.
What Is BPO’s Future, and What Are the BPO Trends?

The future is bullish for the BPO industry. The sector’s access to innovations and advanced technologies will bolster the uptrend. Its growth momentum and popularity among businesses will continue beyond 2030. Notwithstanding its adverse effects, the pandemic has contributed to emerging trends in the outsourcing sector.
Below are some BPO trends seen to change the outsourcing landscape in the coming years:
- Artificial intelligence (AI). Service providers will likely incorporate AI technology into their operations to reach next-level efficiency while reducing expenses. AI solutions can also help human agents and improve the customer experience.
- Cloud-based technology. This refers to services offered through the Internet, including software, networks, server development systems, and databases. Many BPO firms have adopted this cost-effective model since building physical infrastructure is no longer a priority. Cloud computing allows providers to save on operating costs.
- Cybersecurity. Third-party providers know the importance of cybersecurity in protecting computer systems against online attacks. Tighter data security measures are the main priority.
- Omnichannel solutions. Many BPO providers heavily invest in unified communication platforms to combine all channels (e.g., phone calls, email, live chat) and enhance customer interaction, satisfaction, and retention.
- Remote work. Due to social distancing protocols, many service providers have assigned tasks to remote workers. Remote working arrangements reduce operating costs since office spaces are no longer necessary.
- RPA. Third-party providers have used RPA to take productivity to new heights. This technology allows a software robot to perform common tasks so that human workers can concentrate on complex duties.
- Social media management. For years, BPO companies have upgraded their tools and capabilities to deliver various social management services, including monitoring social media activities, responding to customer posts, generating content, and providing business intelligence.
When Should You Outsource?
Many different perceptions surround BPO. Some are against the business strategy, but others are for it. Regardless, BPO providers can help you with your non-core tasks.
Here are some signs and situations that indicate you need to outsource soon:
- When customer calls flood your communication channels. Your business struggles to reply to customers through different channels such as text messaging, email, or phone calls. Third-party providers have ample agents and specialists to resolve your situation.
- When the core business should come first. You should concentrate on business growth and high-value operations. Outsourcing frees up your time as the third-party team deals with the non-core functions.
- When the holidays are near. Sales and other operations get busier during major holidays. Your online store’s high traffic volume means more customers will contact you. A BPO provider can help you handle relevant processes during the period.
- When the overseas expansion is certain. You will need a third-party team to manage customer service and tech support when setting up a subsidiary in a foreign country.
What BPO Best Practices To Follow for Successful Outsourcing
Consider these eight best practices to help you maximize business outsourcing.
BPO best practices cover different segments, from training and workers to security and technologies. Let us start.
1. Pick the Right Agents for High Productivity
Recruit third-party professionals with extensive backgrounds and certifications, if necessary.
Soft skills are vital for effective communication, regardless of the type of outsourced work. Contractors should be:
- Persuasive. They can sway customers to buy products or post positive reviews.
- Knowledgeable. They can sufficiently answer customer or client questions about the company, products, services, and tasks.
- Effective problem-solvers. They can properly identify customer problems and promptly provide solutions.
- Empathetic. They can understand customer concerns.
- Good team players. They consistently contribute to the team.
2. Organize a Versatile Team for Improved Efficiency
Use these tips when forming a third-party team to increase efficiency:
- Define the proper team size. Your team must include an experienced team leader or supervisor, specialists with a few top performers, and a consultant to assist the team.
- Get the appropriate people. Your team must consist of seasoned specialists and fresh hires. Experienced team members are creative and composed, while rookies are teachable, flexible, and energetic.
- Promote collaboration. Encourage openness, teamwork, honesty, and confidence. These qualities help strengthen team morale.
3. Invest in the Latest Technologies To Streamline Workflow
The following are some advanced technologies to obtain:
- Cybersecurity is an effective tool against data intrusions, scams, and theft.
- AI simulates human intelligence in digital machines and devices to cost-effectively increase team performance.
- Cloud networks enable remote cloud access to all software and tools used in outsourced work.
- RPA lets the third-party team spend more time on complex and critical processes.
- Omnichannel integrates all modes of communication, such as phone calls, social media, email, and live chat, into a single platform.
4. Guarantee Data Security To Avoid Financial Losses
Ensure the third-party provider has the cybersecurity technologies to protect critical and sensitive consumer, client, and company data.
The BPO provider must take high security and privacy measures to safeguard personal information, including:
- Bank account numbers
- Residential addresses
- Credit card numbers
- Insurance details
- Investment accounts
- Medical records
- Payroll
Data security practices must also comply with government regulations and industry standards. Noncompliance leads to severe fines or litigation. Additionally, compromised data due to weak security can affect your company’s image and bottom line.
5. Communicate With Customers or Clients via Their Preferred Channels
Customers, end users, and clients have preferred modes of communication according to their demographics.
Check these guidelines:
- Phone calls. Baby boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, heavily depend on fixed phone lines (telephones).
- Email. Generation X, born between 1965 and 1985, and baby boomers prefer this communication method.
- Live chat. Generation Z, born between 1997 and 2012, opts for this channel.
- Social media. Gen Z and millennials, born between 1981 and 1996, are heavy users of these networks.
- Messaging apps. Gen Z and millennials are frequent users of this platform.
6. Implement a Strong Staff Training Program To Enhance Service Quality
BPO companies must provide high-quality service by training workers to reach their maximum potential. Both new hires and experienced agents need continuous skill development.
Consider the following training pointers for a better team:
- Team up rookies with veterans. Job shadowing is a tried-and-test method to shorten the learning curve of new hires and underperformers.
- Never say no. Urge every team member to give customers or clients positive answers regardless of their questions or requests. Allow them to be creative but honest in their responses.
- Simulate situations. Sharpen agents’ decision-making skills through role-playing. Give them real-life and challenging scenarios that need suitable solutions.
7. Assure Staff of a Rewarding Career To Retain Talent
BPO providers must retain deserving and skilled workers to provide consistently high-quality service.
Note these tips to help agents develop long-term career plans:
- Launch a leadership training program. Providing leadership initiatives shows the company’s sincerity in advancing interested and deserving agents to managerial roles.
- Ask about their career paths. Engage with agents and learn more about their career plans. Discover how they view themselves someday in the organization.
- Offer incentives and rewards. Generously compensate high performers and others who bring in income. Offer incentives to dependable and loyal staff as well.
8. Focus on the Metrics That Matter To Optimize Outsourcing
Track relevant KPIs to maximize services. Pay attention to metrics that measure service levels. Some examples include:
- First call resolution (FCR) measures how fast an agent resolves a customer’s needs on the first call. The greater the FCR rate, the faster the resolution.
- Agent schedule adherence indicates whether agents comply with their assigned schedules. A low rate can result in poor customer service.
- Average handle time (AHT) gauges how long or short an agent spends on a customer call. The ideal time is less than six minutes.
How To Outsource Successfully
A BPO guide is complete when it properly provides tips on outsourcing your processes. Follow these seven steps to work with the right partner:
- Specify goals and needs. Examine and develop outsourcing strategies with partners, stakeholders, employees, and other decision-makers. Determine the appropriate team size, pick the necessary communication channels, and define the type of outsourcing that matches your business requirements.
- Evaluate every pre-screened BPO candidate. Conduct detailed research on each prospective third-party company and check its knowledge, skills, and capabilities. Prioritize potential partners with a dedicated team to specialize in your outsourced processes. You must also ask about their data security and privacy protocols.
- Obtain an extensive list of service charges and hidden costs. Ask prospective BPO firms to provide a complete list of service fees and other additional expenses. Review their rates, weigh their package pricing, and perform comparative studies.
- Draft a request for proposal (RFP). It is time to shorten the list of candidates at this point. Prepare an RFP and send it to each short-listed third-party provider. The RFP must have the outsourced work’s coverage, timeline, budget, and solutions.
- Select the provider that can meet all your business needs. Coordinate with your new partner to develop a service-level agreement (SLA) that lists the types of assistance required and other relevant information. The SLA details the outsourcing project’s terms and conditions, including KPIs.
- Keep an eye on the outsourced processes. Track the productivity and efficiency of the third-party team. Ensure it achieves objectives, meets needs, and hits targets. Monitor the KPIs and qualitative factors (e.g., agents’ soft and knowledge skills) to gauge the team’s performance.
- Maintain frequent contact with the BPO partner. Interact with the service provider constantly. Build, increase, and fortify the business relationship for a long-term partnership.
What Is the Difference Between BPO and BPA?
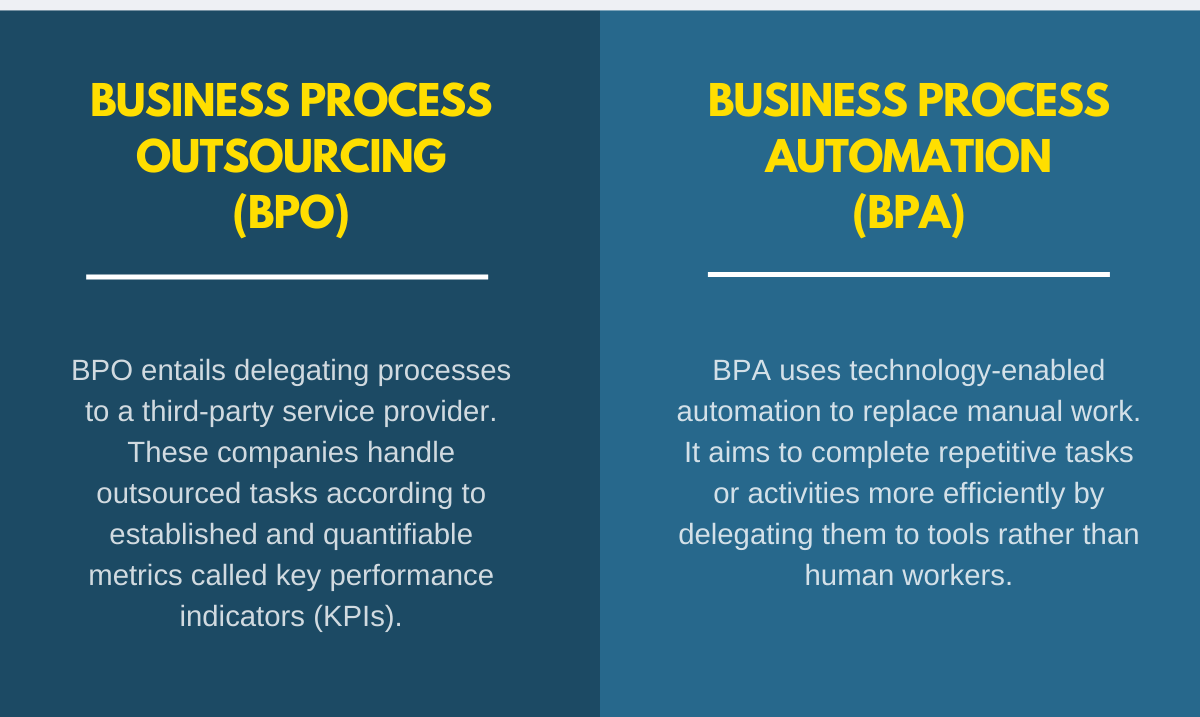
Business process automation (BPA) uses technology-enabled automation to replace manual work. It aims to complete repetitive tasks or activities more efficiently by delegating them to tools rather than human workers. BPA strives to replace live agents and supplement or help them.
BPO entails delegating processes to a third-party provider, while BPA is the process of automating in-house business activities.
Asana identifies the following as the common tasks to automate with BPA:
- Project tasks – moving and assigning tasks, setting and shifting due dates
- Communications – sending project reminders, updates, and post-meeting minutes
- Data entry – reducing duplicate data, importing forms, flagging data inconsistencies
- Sales orders – personalizing marketing campaigns, tracking market trends
- Payroll – providing pay stubs to team members, helping employees with tax filing
- Lead nurturing – sharing content with potential customers, generating campaign workflows
The Bottom Line
You should know what BPO is better at this point, its history, current state, and future trends. Understanding business process outsourcing—the advantages, disadvantages, types of services, best practices, and ways to choose a BPO service provider—is the first step in achieving more success and growing your business.
Outsourcing has evolved from doing simple tasks in certain sectors to getting involved in sophisticated strategic decisions. As the BPO market transforms, third-party contracts also adjust to thrive. Whether a startup or an established business, stay ahead of the curve by reading up on related, updated, and comprehensive pieces of content such as this guide.
Do you want to know more about outsourcing and what BPO is? Let’s connect!





