IN THIS ARTICLE
Table of Contents
Businesses need information technology (IT) support to succeed. It helps them meet requirements and achieve operational goals. As a key function in your business, you should update it regularly to avoid obstacles in your workflow.
This guide discusses IT support and how it helps an organization. It explores the composition of a technical team, types of technical assistance, measurements, and issues.
It also introduces you to IT support outsourcing, a business practice gaining ground due to the advantages it offers to companies of all types and sizes.
Keep reading to learn more!
What Is IT Support?
Simply put, IT support is the help or assistance technicians or computer specialists provide for end users, customers, or employees concerning technology-related systems, devices, or equipment. It offers them answers or solutions whenever they face technical issues.
When a problem arises, end users contact an IT professional, who typically needs access to their devices for diagnosis and troubleshooting. This IT professional analyzes and solves the technical issues on-site (physical location) or off-site (remote location), depending on the IT support team’s setup.
IT support plays a bigger role in an organization than just technical assistance. It ensures that the entire company’s information system operates smoothly and regularly. The technical team oversees hardware, software, networks, and other technical activities daily to manage the flow and use of information.
Who Are the Members of an IT Support Team?
An IT support team generally consists of agents (representatives or specialists), developers, programmers, engineers, and consultants skilled in different technical fields.
The size of the team depends on the size of the organization. An IT support team in a small business has a manager as the head. Meanwhile, a large company appoints a chief information officer (CIO). The IT department’s executive is responsible for strategy, planning, and overall management.
Next in the hierarchy are the other technical professionals who accomplish daily tasks such as:
- Testing and reviewing the latest technologies
- Asking questions to resolve a problem
- Solving network issues
- Troubleshooting, diagnosing, and correcting faults
- Supporting the deployment of new systems or applications
- Installing and configuring software, hardware, and networks
- Handling multiple cases simultaneously
- Offering timely and accurate customer or user feedback
- Performing electrical safety checks on equipment and gadgets
- Determining solutions for computer systems
- Preparing procedural records
- Replacing or fixing parts and components
- Designing security applications
- Following up with customers or clients to ensure the resolution
How Can IT Support Help Your Company?
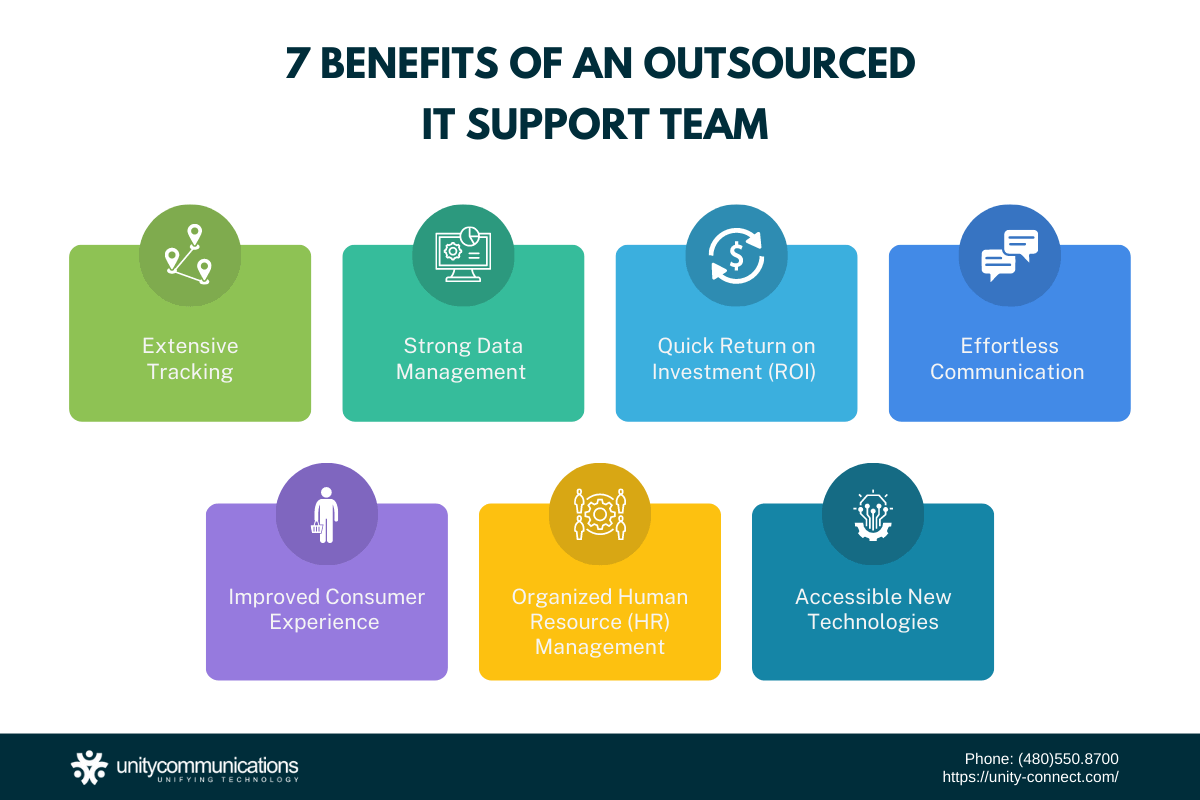
Below are the benefits of having an IT support team in an organization:
Extensive Tracking
Monitoring developments within your organization is vital. Management should be aware of daily operations and customer service activities at every point.
A closely and regularly supervised IT system, supported by workflow automation software, can assist your business in various ways. IT support hones facilities and logistics planning, improves internal auditing, raises quality control, and delivers higher user satisfaction.
Vigilant IT support reduces common and costly technical issues, including data loss or breaches, system crashes, and network failures. An IT team provides assistance and fixes problems immediately before they can inconvenience you or your customers. Addressing issues right away prevents escalation or further damage.
Watching the IT system closely also lowers potential revenue loss from system interruptions and downtime. The team is right there to respond whenever things go wrong.
Strong Data Management
Your organization contains confidential and critical information such as employee salaries, compensation, insurance, personal profiles, and tax details. IT support can competently manage data to provide executives with timely and accurate information for better decision-making.
IT professionals know how to design and execute stringent data protection policies. They ensure that data is stored securely and accessible only to authorized personnel. Technical experts oversee data exchange, such as when files are deleted, retained, or shared across networks.
Additionally, an IT support team can keep you updated on data compliance laws and the latest industry standards. It assures that no data group is isolated or siloed, allowing for a smooth and secure flow of information.
Quick Return on Investment (ROI)
Investing in IT support reduces downtime, thus saving your business from substantial financial losses regardless of your industry. For instance, the average car manufacturer loses $22,000 per minute during production stoppage. Unexpected downtime costs industrial manufacturers about $50 billion per year.
An effective IT support team can also shorten the problem-resolution period, enabling you to save money, time, effort, and other valuable resources. It can maximize the available systems and tools to achieve better productivity, performance, and revenue.
IT professionals take advantage of cloud-based technologies. They store and access all required tools and applications on a single, secured platform, significantly decreasing maintenance and data management expenses. These factors contribute to improved ROI.
The benefits of faster and higher ROI are as follows:
- Your business can last for a longer time.
- You will see the positive results of your capital expenditure before long.
- You handle your financial resources more prudently.
- Your company experiences improved income with reduced expenses.
Effortless Communication
As your business and consumer base expand, you need more interaction points to accommodate your growth. A capable IT support team can deploy multiple communication channels simultaneously, ensuring continued and timely service delivery and smooth operations.
Here are examples of communication channels:
- Standard phones are fixed-line phones or telephones used for making voice calls.
- Email can send electronic messages about noncritical requests and complaints. You can also transmit files, images, and documents through email.
- Short Message Service (SMS) lets you quickly send short text messages to employees or customers using smartphones and other mobile devices.
- Chatbots are automated software that can answer common and basic questions, helping your customer service, help desk, and sales support staff.
- Voice over internet protocol (VoIP) telephony permits you to call anyone with high-speed internet and a VoIP phone or device.
- Social media lets you communicate with consumers and personnel via social networks such as Facebook, TikTok, Twitter, and Instagram about your company’s products and services.
- Live chat enables your staff to interact in real time with anyone visiting your website for product, service, or company questions and concerns.
IT support can establish a single omnichannel system, removing the need to install and learn different platforms for each communication mode. This system unifies and synchronizes all video, audio, and text into a single platform for seamless customer and user interaction.
Improved Consumer Experience
A reliable IT support team can enhance customer satisfaction by offering end users multiple communication channels (as stated above) and efficiently addressing their product or service complaints.
The perks of an excellent customer or user experience include the following:
- Better customer retention. IT support specialists are skilled in handling technical issues and customer relations. Establishing rapport and familiarity with customers is their strong suit.
- Better accessibility for consumers. Technical support agents are reachable via different communication channels. Customers can interact with agents anytime, even during holidays, weekends, or late nights.
- Decreased user worries. Efficient IT support representatives help users solve issues as quickly as possible. They immediately raise support tickets to convincingly address concerns.
- Higher regard for customers. An experienced IT support agent asks the right questions to learn more about the end user and their needs. Agents get customers’ feedback, suggestions, and opinions before finishing the conversation.
Organized Human Resource (HR) Management
A third-party vendor providing an IT support team can develop and customize hiring procedures and policies for more efficient personnel management. It can automate processes to reduce paper-based documents that are now impractical, tedious, and slow.
The team can design and implement an HR management system (such as an in-house online portal) that all employees can access and use. The system includes employment details, job descriptions, contracts, personal profiles, benefits, and individual work performances.
With an HR management system, you can:
- Offer employee self-service. Employees can update their personal and job information without needing to visit the office or talk to the HR team. This gives HR staff more time for urgent and complicated activities.
- Automate basic tasks. The HR software takes care of repetitive and time-consuming tasks. It automatically gathers, tracks, and reviews employee data. This helps the HR team with processes such as monitoring staff working hours and paid time off, computing figures (e.g., salaries, taxes, and deductions), and conducting evaluations.
- Help employees perform better. The HRM system is an excellent platform for sharing training sessions, articles, and other upskilling resources to improve productivity.
Accessible New Technologies
An IT support department can use the latest technologies to accelerate and streamline processes. IT professionals are familiar with and trainable in advanced applications, systems, and platforms that boost workflow and output.
Technical support can harness cloud technology to take customer or user experience to a new level. A cloud-based infrastructure incorporates multiple applications such as customer relationship management (CRM) software, for a smooth and organized workflow and customer service.
An example of CRM software is Kommo, which integrates many marketing and communication tools into the same place, and helps you in managing your clients and leads.
Check out the other sophisticated technologies you can leverage with an IT support team:
- Cybersecurity safeguards your data against cyber intrusions, breaches, threats, and other cyberattacks. A service provider has the experience and skill to offer continuous cybersecurity solutions.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) imitates human intelligence in computer systems, machines, and devices. AI is cost-effective and assists in improving output and efficiency. It can handle tedious tasks that hamper team productivity.
- The internet of things (IoT) is the interconnection of multiple digital devices, appliances, and equipment that use the internet to instantaneously share information. Higher connectivity leads to faster response time due to ease of data access.
- Robotic process automation (RPA) enables software robots that perform basic, repetitive, and burdensome activities. RPA enables employees to concentrate on high-value tasks.
- Cloud computing is a platform that provides various computing services, including data storage, networking, software, tools, and applications, through the internet. You can obtain, store, and share information in a secure environment.
What Are the Two Types of IT Support?
IT support can be swarming and tiered technical support. Explore the details below to know the difference.
Swarming
Swarming support lets a technician take on a certain technical issue from beginning to end. The technician looks for the right resources and materials to address the problem. If they cannot immediately close the ticket, they “swarm” with their colleagues to find the solution.
The size of the IT support team and the product or service type supported determines how big or small your swarm should be.
A small-sized business of up to 50 employees involves mostly everyone in a swarm together. Technicians regularly check incoming tickets, resolve tickets to the best of their abilities, and let others in the swarm handle more complex issues.
Medium- and large-sized organizations with at least hundreds of workers are more organized. Their swarms are grouped into two categories: local and severe.
- Local swarm monitors incoming tickets and chooses the quickest and simplest issues to resolve. It typically comprises an agent and a specialist.
- Severity swarm specializes in more complex, tougher, and more sensitive technical concerns that the local swarm cannot handle. Only specialists can be part of this group.
Tiered Technical Support
IT support is structured into five levels to address various technical requests, issues, and problems.
- Tier 0 (T0) support enables end users to resolve IT issues without contacting a technical support representative. The company website houses this tier. It contains video tutorials, search functions, frequently asked questions (FAQs), blog posts, and product or service information.
- Tier 1 (T1) support gathers consumer data and information, evaluates issue details, and provides feasible solutions. T1 agents handle 75% of all technical issues by applying fundamental IT knowledge and software tools. Agents in this tier help customers with basic problems such as fixing passwords and configuring operating systems.
- Tier 2 (T2) support fixes 25% of technical problems beyond T1’s capability. T2 members have better technical knowledge and skills.
- Tier 3 (T3) support consists of the best IT support specialists. They deal with crucial and difficult technical problems that T2 cannot solve. T3 technicians develop new solutions to challenging incidents and share them with the lower tiers.
- Tier 4 (T4) support is an external service provider. You contact this support tier when the root cause of an issue is a product or service defect. T4 supplies the necessary replacement parts and components.
Swarming vs. Tiered IT Support: Advantages and Disadvantages
Let us look at the benefits of the two types of IT support.
| Swarming | Tiered IT Support |
|---|---|
| Smaller backlogs. Project or task resolution is faster in swarming support because agents of different skill levels work on issues together. | Suitability for large volumes of common tasks. Tiered support is effective when most technical issues are simple and basic. Generalist T1 support agents are maximized in this setup. |
| High collaboration. Agents from separate teams work together to achieve a common objective. Swarming promotes cooperation, communication, and a close working relationship. | Quick implementation. Tiered support is a widely accepted approach in many industries because it requires less training for a new support team. Tier-based support is affordable and easier to deploy. |
| Faster resolution. Swarming team members have different technical experiences and backgrounds, so effective collaboration saves time and reduces completion time. | Available training resources. Tiered agents can access instructional materials and formal courses to improve their soft and technical skills. |
| Increased knowledge-sharing. A technically diverse, swarming team allows members to learn from each other and acquire new skills while resolving issues. | Compatibility. The tiered setup matches the structure of many organizations, especially large-scale enterprises. |
On the other hand, let us check the drawbacks of the two types of IT support.
| Swarming | Tiered IT Support |
|---|---|
| Lack of structure. The swarming setup is unstructured, so pr0oper documentation is a challenge. Higher-level IT specialists are likely preoccupied with easy but tedious tasks meant for technical generalists. | More ticket backlogs. Tickets are escalated and queued if T1 agents cannot close them. Ticket escalation through tiers might result in longer wait time for end users. |
| Constant training and updates. Re-training and upskilling all support members might be a regular requirement. This is necessary to enable swarms to competently handle various issues. | Limited skill and knowledge sharing. The tiers are isolated or siloed. Agents do the same tasks most of the time. T1 and T2 agents gain knowledge only when T3 shares new solutions from unique cases. |
| Incompatibility with a large team. Using the swarming method on a large team can be chaotic and confusing. Not all agents can be jacks of all trades in a big organization. | Less motivation over time. Tiered agents might lose a sense of responsibility, ownership, or accountability in the long run. Agents likely escalate tough cases to the next tier instead of finding a solution. |
Swarming vs. Tiered IT Support: Which IT Support Model Is Best for You?
Choose the swarming approach when:
- Running a small technical support team
- Aiming for a zero or small backlog
- Building a close working relationship among employees
- Planning to increase resolution time
- Dealing more often with common technical issues than complex ones
- Teaching and training the less experienced members
- Empowering the IT staff through higher accountability
Go for the tiered support method when:
- Managing numerous IT professionals
- Resolving mostly repetitive, basic, and simple issues
- Matching the organization’s structure
- Requiring more systematic and direct records of all processes
- Needing less employee training and orientation
- Looking for a support system that is quick and affordable to deploy
- Experiencing fewer issues with the current product or service
How Do You Assess IT Support Performance?

The following are some key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge a technical support team’s efficiency:
- First call resolution or first contact resolution (FCR) rate refers to the percentage of support tickets completely resolved in the first contact. Support tickets provide various details so technical support agents can resolve the issue immediately. A high FCR rate raises user satisfaction and reduces the cost per ticket.
- Cost per ticket is computed by dividing the IT support’s monthly operating expenses by the monthly total number of tickets. The technical support team must keep the cost per ticket below the level set by management. High costs mean long resolution time, weak team performance, and ineffective training programs.
- Ticket volume trends pertaining to the total number of tickets the IT support team manages and the pattern of those tickets over time. Evaluating the trends is essential to know whether the IT team requires support and assistance. It also helps you determine your next actions or decisions.
- Customer satisfaction score (CSAT), also called end-user satisfaction, is a gauge for technical support efficiency. This metric measures how happy users are with a product, service, or customer support interaction. CSAT is measured through a customer satisfaction survey. The higher your CSAT score, the happier your consumers are.
- Change success rate is the ratio of the total number of effective changes and the total number of changes implemented in a given time. Such changes include replacements or adjustments to the organization’s systems or processes. Your goal is to attain a higher ratio to show how successful new implementations are.
What Are the Important IT Support Features?
Consider the key capabilities, technologies, and features your IT support team must have to raise performance and productivity:
- Collaboration. The IT team must work together across all levels and in any situation. Assigning, accessing, tagging, and prioritizing tasks must be flawless to provide excellent customer satisfaction. Communication lines must be open to encourage information sharing between tiers.
- Self-service. This is a must-have feature that reduces the workload of the technical support team. With self-service options, end users can find solutions to their technical issues without submitting a support ticket. They can access this option through a dashboard, an online resource, or the company website.
- Automation. Like self-service, this capability helps the IT support team focus on more critical tasks. Automated systems handle common and repetitive processes. They send scripted replies to help resolve basic issues faster, improving work efficiency and reducing ticket backlogs.
- Lice chat. Constant communication with customers, users, and colleagues is vital for updates and information. Live chat is a faster and more convenient method of communication than phone calls. The team can also post links, canned responses, and useful articles on the messaging platform.
- Reporting and auditing. This feature enables the IT support team to send and track reports of its daily operations and performance. Regular reporting details and analysis of KPIs for further team improvement. Auditing ensures that the technical team meets compliance standards.
- Integration. This capability lets the team integrate additional technologies required to optimize organizational workflow and customer service. Integration is done by application programming interfaces (APIs) that enhance user experience. APIs can be deployed without disrupting business operations.
What Are the Technical Issues That IT Support Addresses?

Technical assistance is necessary when software, hardware, or network problems arise. The following are common issues that IT support can resolve:
- Lost passwords. A technician assists users who forget the passwords to log on to their desktops, emails, and work accounts. They can recover or reset the passwords or gain access to the network for further assessment.
- Poor computer performance. Inefficient desktops, laptops, and digital devices frustrate users. They cause delays and hurt employee productivity. An IT professional can find and address the source of the problem. The issue can result from insufficient computer memory, virus infection, or glitchy software.
- Data loss. Your organization can lose data because of a user mistake, cyberattack, hardware breakdown, network malfunction, or power failure. But the IT support team implements adequate recovery and backup strategies, restoring data to save money, time, and effort.
- Remote work connection. An IT support team goes beyond managing and connecting databases so that in-house employees can access, use, and share information. It also connects remote workers. Remote employees can access data and company resources and communicate continuously, even when performing their jobs in distant locations.
- System maintenance. An IT support team ensures that hardware and software tools are in good condition and running smoothly for the company’s daily operations. It monitors all points and applications to prevent downtime. The technicians also regularly check vital hardware devices and install software patches or updates.
What Are the Concerns That IT Support Faces?
IT support professionals encounter hurdles in adapting to technological advancements and the new normal. Below are some examples:
- Digital transformation. Considered a disrupter, this process involves incorporating digital technology into all business segments to accelerate change. This organization-wide undertaking compels an IT support team to keep pace with the rapid digital shift and to implement the latest technologies.
- Cybersecurity. Online attacks are increasing in size and complexity, but the IT industry lacks the workforce to address them. Organizations take security seriously. An IT support team should be ready to handle cyberattacks anytime, regardless of the security measures in place.
- Insufficient remote-friendly infrastructure. Social distancing and lockdowns due to the pandemic have resulted in the rise of remote working arrangements. But many companies fail to equip workers with the tools and technologies needed to do their tasks efficiently. The IT support team has to make the most of the resources available.
- Shortage of skilled IT professionals. The demand for IT professionals worldwide continues to outpace the supply due to factors such as heightened business competition. Finding the right technical talent affects the performance of an IT support team. Fewer skilled employees mean lower output.
What Is the Future of IT Support?
The latest Spherical Insights & Consulting report says the IT services market worldwide is seen to hit $2.5 trillion by 2030, more than double the 2021 value of around $1.1 trillion. This will register a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of almost 6% in the forecasted period. It attributes the expansion to the increasing business demand for IT infrastructure.
It adds that many enterprises rely on IT services for data analytics applications. Technology companies also turn to IT professionals to support their operations. Such demand will further fuel the expansion of the IT services sector. Adding to these are the changes in work culture via telecommuting, the continued maintenance of the organization’s IT systems, and the pandemic.
The report also states that the growing use of cloud-based platforms will contribute to the rise of IT services. Cloud computing leads to industry growth as the technology provides various business advantages, including decreased IT expenses, higher scalability, bigger storage capacity, and accessible automated features.
The study points out that the North American region (U.S. and Canada) will continue to corner the biggest chunk of the global IT services market because of the widespread adoption of innovative technologies. Major players have also established their market presence. The Asia-Pacific region will experience the biggest growth rate owing to the rise of smart devices.
What Are In-house and Outsourced IT Support?
In-house IT support is running your own technical department. Technicians, agents, and representatives work on the business premises, typically full-time. Under your supervision, the team uses internal IT policies and methods to achieve business goals.
In contrast, outsourced IT support involves hiring a third-party vendor, such as a business process outsourcing (BPO) company or a managed service provider (MSP). This external vendor manages your technical operations for a fee. It also has greater control over the delegated processes, executing its standards to ensure the timely and accurate delivery of services.
What Is the Difference Between In-house and Outsourced IT Support?
Explore the difference between in-house and outsourced IT support in the table below:
| In-house IT Support | Outsourced IT Support | |
|---|---|---|
| Hiring and Training |
|
|
| Service Quality Level |
|
. |
| Costs |
|
|
| Market Reach and Language Support |
|
|
| Supervision, Reaction, and Information |
|
|
How To Outsource IT Support the Right Way
The following are seven best practices to properly outsource IT support and other back-office outsourcing services:
- Identify business goals and technological requirements. Lay out your outsourcing strategies for IT support and discuss them with key decision-makers and employees. Determine the right team size, choose the relevant communication channels, and find the type of outsourcing that suits you (e.g., offshoring, onshoring, or nearshoring).
- Evaluate each potential BPO partner. Conduct thorough research and studies. Gather information on as many service providers as possible and learn about their expertise and experience. During the interaction, ask about their teams’ qualifications and security and privacy protocols.
- Inquire about complete service costs, including hidden fees and extra charges. Ask prospective BPO partners for full rates and other additional expenses. Analyze and compare their costing models and pricing schemes.
- Create a request for proposal (RFP). After the initial evaluations and inquiries, limit the number of prospective candidates. Create an RFP and send it to your short-listed BPO candidates. The document must contain vital details such as the IT support work scope, time frame, budget, and recommended solutions.
- Choose the service partner that best meets your needs. From this point, prepare a service-level agreement (SLA) by listing the IT assistance required and other important details. It must include your and the partner’s terms and conditions, particularly the KPIs.
- Track the outsourced IT support operation. Keep a close watch on the third-party team’s performance and productivity to ensure it meets your expectations. KPIs and qualitative measurements (e.g., agent soft skills and knowledge) are top priorities.
- Keep constant communication with the BPO partner. Regular interaction, updates, and collaboration are necessary when you outsource data entry services or IT support. This builds, hones, and extends the business partnership with the BPO service provider.
How To Find Your Ideal Service Provider
Consider these useful tips to find the best third-party IT support team for your company:
- Excellent track record. Choose a BPO provider that has established and well-known clients. Check its credentials and objective reviews about its services. You will be more confident partnering with a reputable service provider.
- Various IT support services. Opt for a BPO partner providing different outsourced technical support. The service must range from basic (e.g., diagnosing, installing, and troubleshooting) to complex (e.g., digital transformation, network management, and cybersecurity) support. Get all the technical support you need from a single provider.
- Right size. Pick a BPO partner that matches the size of your organization. If you are a startup, team up with a small or medium-sized service provider that can prioritize your outsourced tasks. Similarly, big companies must partner with large third-party vendors.
- Technical credentials. BPO providers with IT or technical accreditations or certifications must be on your list. Examples of credentials are CompTIA A+ certification, Microsoft Certified IT Professional, and Certified Information System Security Professional, to name a few.
- Industry-specific expertise. Hire a service partner with high proficiency in your industry. A BPO company with a broad knowledge of your sector can guarantee better services and solutions.
The Bottom Line

IT support provides a wide range of services. More businesses continue to adopt this strategy due to its proven effectiveness. Having an IT team is not a nice-to-have anymore. Every digitally dependent organization needs technical assistance to operate more efficiently.
But IT support carries drawbacks. It simultaneously offers several benefits and poses some potential risks. Investing in IT support is a matter of taking advantage of the perks and limiting the disadvantages to have favorable results.
Knowing about IT support outsourcing—its difference from the in-house set up and the ways to outsource it properly—is also essential to make well-informed decisions.





