Table of Contents
The difference between offshoring and offshore business process outsourcing (BPO) is a commonly misunderstood aspect of the global supply chain. Business owners and decision-makers often confuse these terms, but they are two different concepts.
This is an unfortunate misunderstanding because knowing the difference between the two business practices enriches your knowledge. It helps you understand their positives and negatives to make an informed decision.
So what is offshoring, and how does it differ from offshore outsourcing? Let’s find out!
The Main Difference Between Offshoring and Offshore Outsourcing
Before jumping to a comparison of these strategies, let us first answer: what is BPO? BPO is the process of transferring internal operations to a third party, which, in turn, manages and oversees the task based on established metrics. Offshore BPO is a type of outsourcing that involves contracting the work to a service provider in an offshore location.
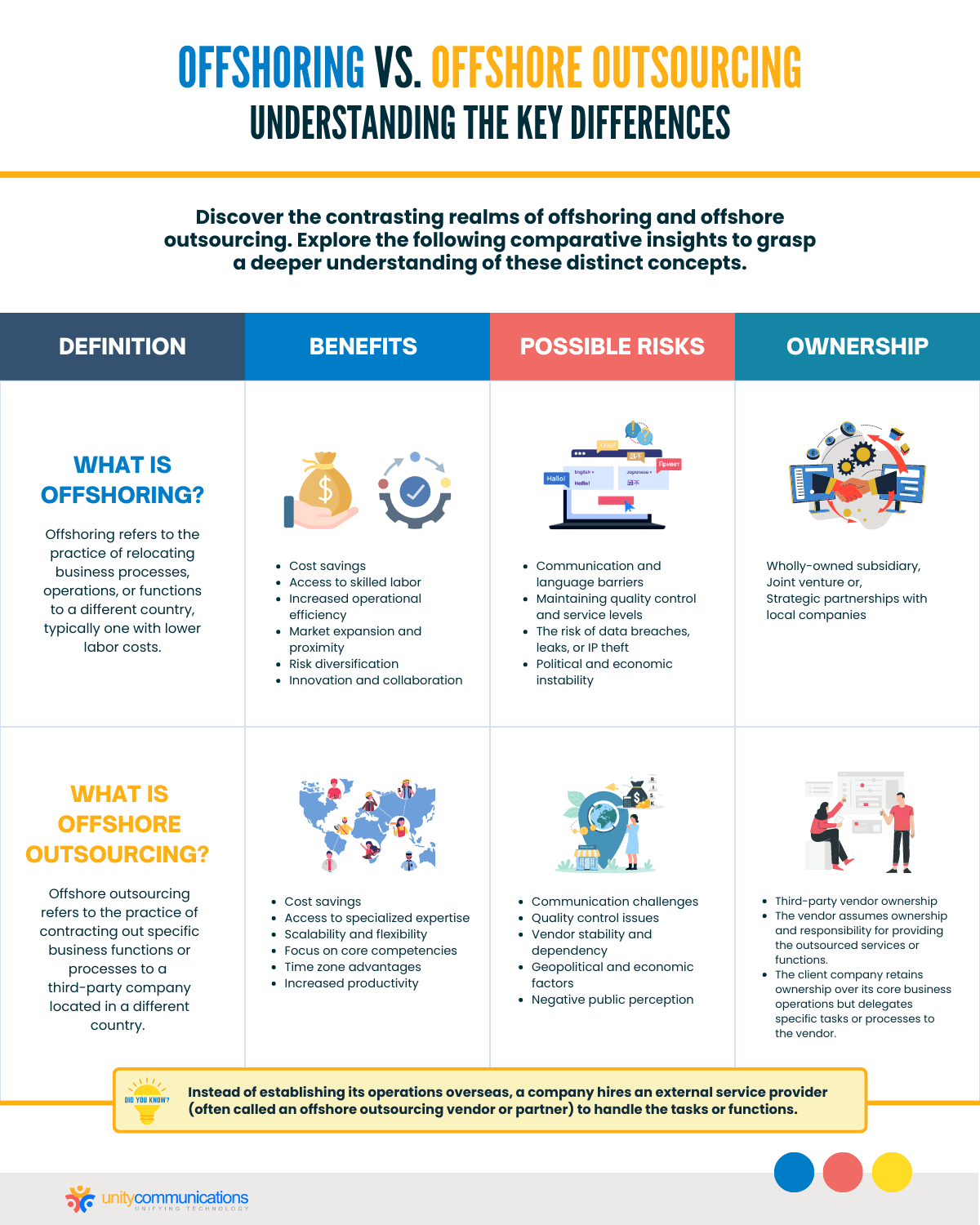
Offshoring and offshore outsourcing are two distinct business activities. What is the difference between offshoring and offshore outsourcing? Here are six ways they vary:
| Offshoring | Offshore Outsourcing | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Offshoring refers to getting work done in a different country. | Offshore outsourcing means contracting the work to a third party in a faraway country. |
| Benefits | Benefits include reduced costs, higher availability of skilled workers, and better productivity. | Companies from developed countries outsource to leverage specialized skills, cheap labor, and cost efficiencies. |
| Risks and Criticism | Offshoring often receives criticism for transferring jobs. Its risks include language barriers, differences in time zones, geopolitical risks, and communication issues. | Outsourcing risks include increased reliance on external providers, misaligned interests between third parties and clients, and missing in-house knowledge about business operations. |
| Ownership | The parent company completes the work. | The parent company does not complete the work. Instead, they assign the entire division or operational unit to a third party. |
| Outcome | Offshoring is a geographic movement-related activity. | Offshore outsourcing is a strategy to streamline an organization’s workflow. |
| Motivation | Cost savings and increased profitability are the primary motivations for offshoring. | Outsourcing’s key motivation is to allow companies to focus on areas of expertise. |
Still confused about what offshoring is? Let us expound on the details to better understand this strategy.
What Is Offshoring?

Offshoring, also known as captive offshoring, refers to the practice of moving a company’s business operations from its home country to a foreign location; one can explore different ways to move out of state in accordance with the company’s best demographic needs. Multinational companies (MNCs) establish subsidiaries in offshore countries to take advantage of different labor laws, cost savings, and improved resource access. This strategy is commonly employed for various reasons.
Thanks to advancements in telecommunications infrastructure and shipping technology in the late 20th century, conducting work in foreign or developing countries became more efficient.
One typical aspect of businesses shifting offshore is manufacturing. The cost savings achieved through offshoring contribute to increased profitability for companies. These savings are then passed on to customers through more affordable products.
Another advantage of offshoring is the availability of skilled human resources in the destination region. For instance, the Philippines boasts a substantial talent pool, with 14 million individuals proficient in English.
How Does Offshoring Work?
Captive offshoring entails establishing its own captive site or subsidiary in an offshore location and hiring local individuals as its employees. The remainder of the organization’s business operations continue to function in its home country. A multinational corporation (MNC) can create internal centers or subsidiaries in another country while retaining complete control and ownership.
In contrast to outsourcing, captive offshoring primarily involves geographic aspects. Products are expensive in Western countries due to the high labor costs associated with their production and distribution. Conversely, the availability of low-cost labor in developing nations forms the foundation for a cost-effective economy.
Captive offshoring capitalizes on cost disparities by relocating factories from Western nations to more affordable economies, allowing for the sale of products at significant discounts. Coupled with advancements in technology, offshoring contributes to reducing consumer goods’ costs.
What Is Offshore Outsourcing?

Offshore outsourcing involves assigning business processes to an external vendor in the developing world to increase efficiency and save money. Companies outsource certain tasks or processes to BPO companies in offshore countries where labor costs are cheaper.
The term entered the business lexicon in the 1980s. As companies grew in the second half of the 20th century, they required more specialized skills and found that third-party vendors could accomplish work faster and more efficiently. This BPO trend led to hiring external providers to oversee business functions where the client lacked specialized skills.
Offshore outsourcing has become increasingly popular in recent years, with companies citing benefits such as improved workflow flexibility, greater productivity, and lower operating costs. The global IT services outsourcing market alone will be worth around $1.06 trillion by 2030, with the Asia-Pacific region having the largest market share.
The benefits of offshore outsourcing are:
- Not needing to handle non-core functions;
- Focusing on core competencies;
- Cutting up to 70% of labor costs; and,
- Achieving labor flexibility and sustainable scaling.
How Does Offshore Outsourcing Work?
Offshore outsourcing can come in the form of shifting a business division to an external party and buying the services back or selling a physical plant to a supplier to buy back services or products. A commonly outsourced function is customer service.
The core idea is to transfer transactional activities to experts to allow organizations to focus on their expertise.
Offshore outsourcing is the basis of decades of trade. Companies that outsource achieve greater specialization in areas that earn them the most profit. Outsourcing, in turn, generated significant wealth for the global economy.
So, is outsourcing a good idea? Is the BPO call center worth it?
Yes, outsourcing is absolutely worth it, but it poses several downsides. When you assign your tasks, you transfer knowledge to an outsider, which can lead to data security issues.
The Bottom Line
Hopefully, this article will answer what offshoring is and the difference between it and offshore outsourcing.
Understanding the difference between the two terms is important. Both offshoring and offshore outsourcing have distinct economic and moral implications, and they offer their own business advantages.
Are you looking for an offshore outsourcing partner? Let’s connect to discuss custom solutions for your business.




