IN THIS ARTICLE
Table of Contents
Market fluctuations and increasing competition have made outsourcing necessary for businesses. Companies can outsource certain business processes or partner with a managed services provider.
Established business process outsourcing (BPO) companies offer innovative solutions and state-of-the-art technology.
This article covers the different types of BPO based on location, work areas, tasks, and supply chains. It also discusses the pros and cons of each type and provides actionable advice on choosing the right model for your business.
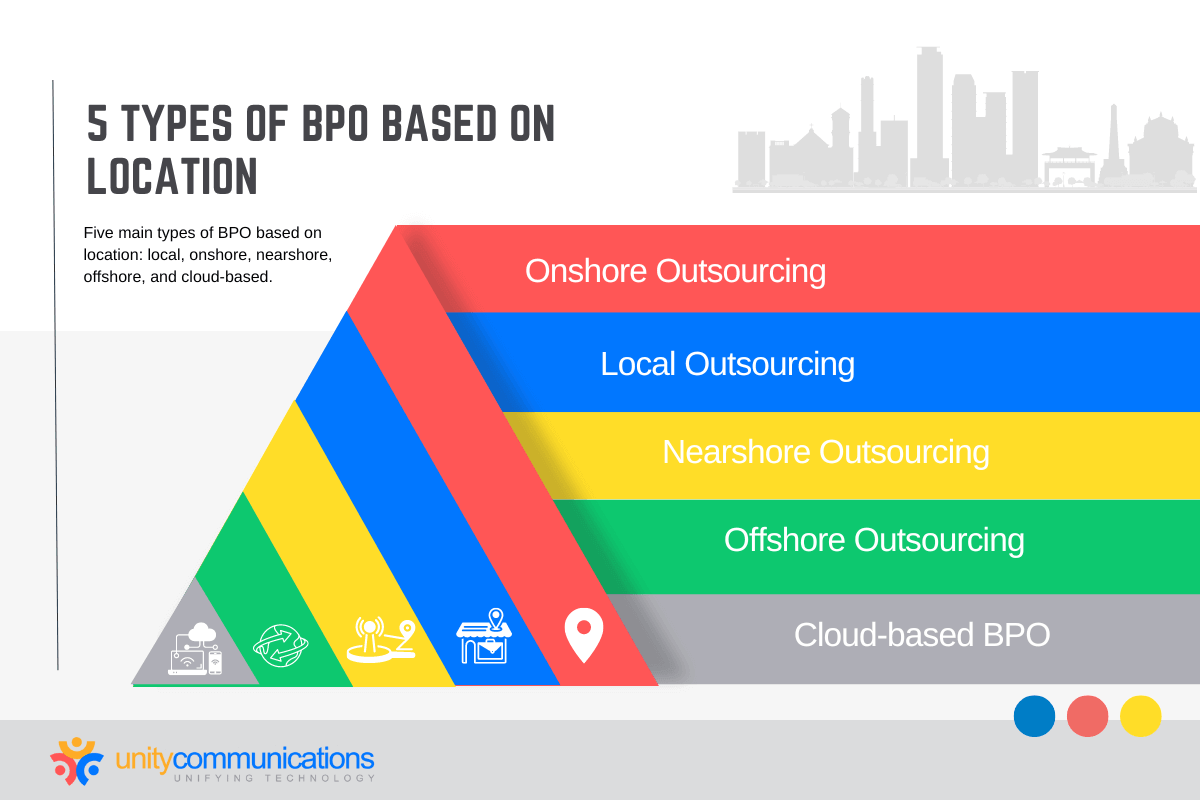
Types of BPO Based on Location
Before diving into its types, let us first answer: what is BPO? BPO involves delegating certain functions to a competent third-party vendor. The term was originally associated with manufacturing companies subcontracting supply chain portions.
There are five main types of BPO based on location: local, onshore, nearshore, offshore, and cloud-based.
Onshore Outsourcing
With onshore outsourcing, you hire a BPO company in the same country where you run the business. For instance, you are running a Florida-based company that employs a Chicago-based service provider. Onshore BPO firms operate in the same time zone as their clients or with a slight, almost negligible time difference.
Pros
| Cons
|
Local Outsourcing
This is when the BPO company is located near your city or within driving distance. This model is ideal because you can meet the third-party team, assess their operations, and visit the site. But this approach is the most expensive option since you cannot leverage economies of scale.
Pros
| Cons
|
Nearshore Outsourcing
Nearshore outsourcing is when a business hires a vendor located in nearby countries. A U.S.-based company outsources to a firm in Mexico or Central America where workers speak English as a second language or are already familiar with its culture. Nearshoring is less cost-effective than offshore outsourcing but has minor time zone differences similar to onshore firms.
Pros
| Cons
|
Offshore Outsourcing
This outsourcing—usually shortened to “offshoring”—involves hiring a service provider in a different country. For instance, an e-commerce company in the U.S. outsources customer support to a Philippine-based BPO company.
This is the most common and least expensive type of BPO. Offshore outsourcing helps save up to 70% of labor costs. Some caveats are the differences in culture, time zones, and accents.
Pros
| Cons
|
Cloud-based BPO
A cloud is a new form of outsourcing that turns BPO into a business process as a service (BPaaS) model and transforms the industry from a service provider to a planner.
One example of a cloud-based BPO is a cloud contact center that uses an internet-based facility to handle customer communications. This facility is suitable for large enterprises requiring multiple communication platforms.
The cloud contact center uses voice-over-internet protocol (VoIP) technology for communication. The cloud contact center syncs data with customer relationship management (CRM) systems so that agents get all the updates. Working with a cloud contact center means businesses must provide only a stable internet connection, a workstation, and a headset.
Pros
| Cons
|
Types of BPO Based on Areas of Work
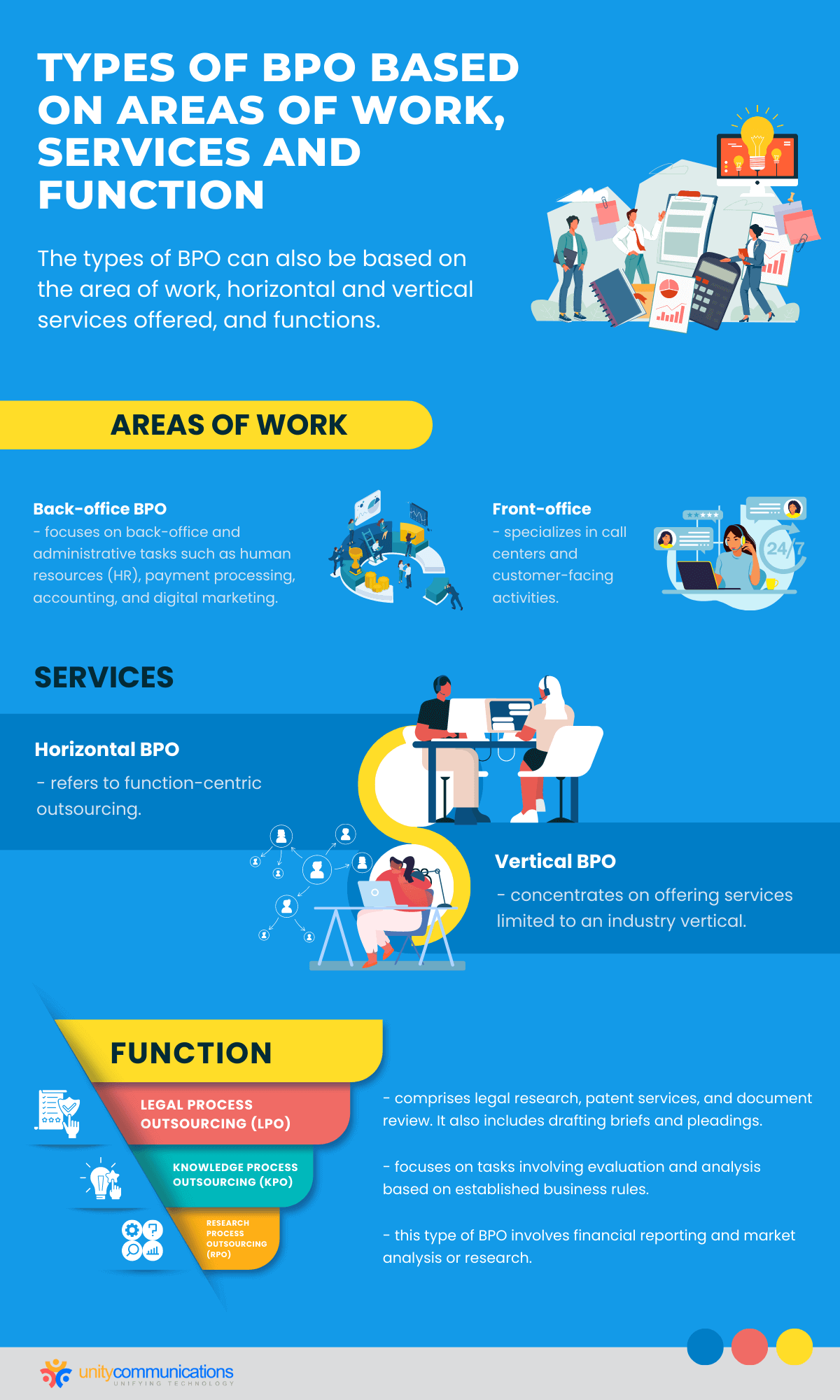
The types of BPO can also be based on the area of work. This can be either back-office or front-office outsourcing.
- Back-office BPO solutions are internal business functions that do not depend on customers. Simply put, customers and back-office workers do not interact with each other. Back-office outsourcing used to involve only administrative activities, but now it offers human resources (HR), payment processing, accounting, and digital marketing.
- Front-office BPO solutions refer to activities that require workers to handle current and potential clients. Call centers and customer-facing tech support are examples of front-office activities. Front-office workers must possess active listening and effective communication skills to successfully manage client interactions.
Types of BPO Based on Services
The categories of BPO services encompass both horizontal and vertical services, which can be classified as follows:
- Horizontal BPO refers to function-centric outsourcing. The service provider carries out particular areas of work across different industry domains. An example of horizontal BPO is outsourced HR, payroll processing, facilities management, procurement, and similar functions.
- Vertical BPO concentrates on offering different functional services in a limited industry vertical or domain. Financial services, retail, manufacturing solutions, and healthcare are examples of vertical business functions.
Here is a table to illustrate how this works:
| Sales | Procurement | Recruitment |
|---|---|---|
| Identify customers | Identify vendors | Identify vacant positions |
| Process orders | Acquire product catalog | Look for candidates |
| Deliver products | Select vendors | Perform interviews |
| Receive payment | Process payment | Pick new hires |
BPO horizontals are function-specific and spread across various industry domains. Processing payments and managing the receipt of payments are examples of horizontal business processes.
Vertical BPO focuses on services within one industry domain, such as sales, procurement, or recruitment. For example, identifying vacant positions, looking for candidates, performing interviews, and selecting new hires fall under the recruitment domain.
Types of BPO Based on Function
Before choosing the right outsourcing model for your organization, let us look at the different types of BPO based on function.
- Legal process outsourcing (LPO) comprises legal research, patent services, and document review. It also includes drafting briefs and pleadings. It involves outsourcing low-skill tasks such as legal coding and high-value qualitative activities. The global LPO market is valued at $11.75 billion in 2022 and could grow in the next decade at a 26% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
- Knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) is a subcategory of BPO that requires higher skills and expertise levels. For example, data entry is a BPO service. But when it involves tasks such as evaluation and analysis based on established business rules, the solution becomes part of KPO.
- Research process outsourcing (RPO) is when an external service provider manages a portion or all of the research and development duties of an organization. This type of BPO involves financial reporting and market analysis or research.
How To Find the Right BPO Model for You

Understanding the significance of selecting the appropriate BPO option and addressing workflow challenges is essential. Here are four practical tips to guide you in tackling these questions effectively:
1. Identify Your Unique Goals and Needs
Every outsourcing service comes with its own set of advantages and risks. Your specific goals and needs will determine your situation’s most suitable outsourcing model. Begin by examining what you aim to accomplish. Are your plans short-term or long-term in nature?
For instance, if cost reduction is your primary goal, offshoring and nearshoring are viable options. However, each model offers distinct solutions. Although there will be unavoidable cultural and linguistic differences, offshoring offers access to a larger talent pool and the potential for round-the-clock operations.
Nearshoring offers similar advantages while mitigating some of the challenges associated with offshoring. On the other hand, if cost savings are not your primary concern and you are solely focused on enhancing output quality, you might consider outsourcing. It’s worth noting that onshoring is less common due to fewer financial incentives.
2. Consider Your Budget
One key element in your decision-making is your budget, or how much you are willing to spend. Budgeting is crucial because the main point of outsourcing is to save money. In fact, 57% of companies outsource to save money.
Remember that this second piece of advice closely relates to the first: the answer depends on your organizational needs. Offshoring and nearshoring are ideal if you are budget-conscious.
3. Determine the Compromises You are Willing To Make
You might experience BPO challenges while outsourcing because each model comes with compromises. Identify which compromises you are willing to make based on your current workflow. Onshore outsourcing sacrifices budget and flexibility to keep output quality high.
With offshore outsourcing, you might encounter more language barriers and cultural differences while potentially compromising control over the function. The upside is that you get more value for your money and a bigger talent pool.
Lastly, nearshoring offers the best of both worlds with cost-efficient services that prevent major cultural and linguistic problems.
4. Optimize Your Workflow
Once you’ve settled on a suitable model, the subsequent task involves fine-tuning your workflow to extract the utmost value from your outsourcing endeavor. The overarching objective of outsourcing is to achieve optimal benefits.
If you opt for an onshore partner, ensure that communication channels remain open, facilitating the full utilization of language and cultural alignment. Conversely, in the case of offshoring, consider configuring your workflow to operate round-the-clock, thereby maximizing overall productivity.
The Bottom Line
Finding the right type of BPO depends on your unique needs. Therefore, it is crucial that you thoroughly assess your operation and set a timeline for when you plan to achieve your goals. Outsourcing is an incredible strategy, whether you want to solve an ongoing problem or work toward a goal.
If you want to maximize the value of your money and engage the biggest talent pool, then offshore outsourcing is for you! Unity Communications is one of the top offshore providers in the Philippines. Let’s connect to learn more about our services.