IN THIS ARTICLE
Table of Contents
When you pay money for a service, you have expectations about its quality and efficacy. Business process outsourcing (BPO) engagements need service-level agreements (SLAs) to manage client expectations and outline the circumstances under which providers are not liable for performance issues and outages.
BPO clients benefit from SLAs because they define the service quality and performance they expect to receive. An SLA details the consequences or remedies when specific metrics are not met. However, learning how to write one is daunting.
Keep reading to learn how to write an SLA, what it should include, and what mistakes to avoid.
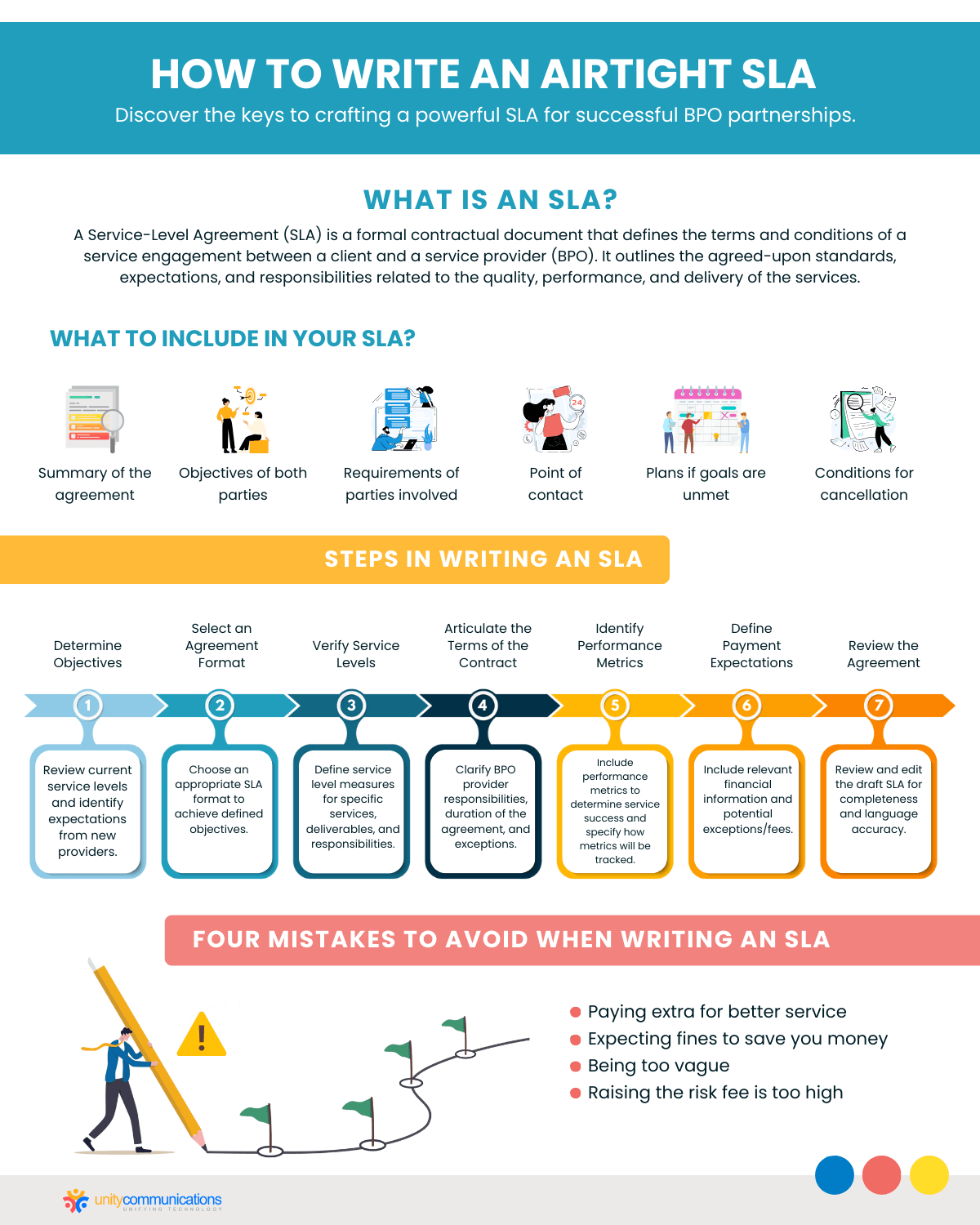
Steps in Writing an Airtight SLA for BPO Partnerships

First, what is BPO? Companies outsource functions to an external service provider to save on costs, improve efficiency, and focus on core competencies. Clients engaged in BPO partnerships must write a service-level agreement to state their required service types and expected level of service. The agreement varies based on services, industries, and vendors.
Before partnering with a BPO provider, clients must carefully evaluate and design a reliable SLA to realize maximum service value. With the steps below, you will know how to write an SLA.
- Determine your objectives. Review the current service level you receive from existing providers and consider what you expect to gain from new ones. If the level of service you need exceeds what you currently get, determine the changes you can make to meet your expectations.
- Select an agreement format. Choose an SLA format that will help you achieve the objectives you defined. You can use a standard SLA template and revise it to meet your needs. You should give some thought to the structure of the SLA, including the format, length, and information to include.
- Verify service levels. Service level measures the output or performance of a service. For instance, a call center might define this as the number of calls answered per hour, while a data center defines this as the number of information inputted into a system. Service levels differ per SLA, so work with stakeholders to verify deliverables and duties.
- Articulate the terms of the contract. Clarify the BPO provider’s responsibilities under the agreement, including their duties, the overall duration of the agreement, and any noteworthy exceptions to the terms. This part of the SLA can also include the service provider’s expectations.
- Identify performance metrics. An effective SLA must include performance metrics determining whether the service is rendered successfully and a statement about how metrics will be tracked, such as during team meetings or using apps. This is crucial because 94% of consumers say excellent customer experiences encourage them to purchase again.
- Define payment expectations. Ensure to include relevant information if the SLA contains elements that might modify the financial aspect of the primary contract. Note potential exceptions and associated fees.
- Review the agreement. Once you have completed the first draft of your SLA, review it for any sections you might need to add or remove. Also, check the language used. If you wrote the SLA independently, reread it for error-free conventions or have it checked by your legal department.
Learning how to write an SLA is easy when you follow best practices. You need not be a lawyer or take months to draft one. If you keep it simple and follow the steps above, you can quickly create one.
What Does an SLA Include?
The details of an SLA differ based on the internal and external agreements of all parties involved. However, an airtight SLA should include the following building blocks, regardless of who the recipient of the service is:
- Summary of the agreement. The overview of the agreement must be the first item on your SLA. What service did the provider agree to deliver? Include the service summary, to whom it is being provided, and how its success will be measured.
- Objectives of both parties. An external SLA—between clients and vendors—primarily states the client’s goals. The BPO provider must work to meet the client’s needs through their service.
- Requirements of parties involved. SLAs should include what each party needs to perform their duties. In SLAs for outsourcing engagements, your needs might go beyond the service rendered. You might require 24/7 support, weekly reporting, or consulting.
- Point of contact. Who is in charge of making sure objectives are met? In this section of the SLA, sort out who talks to whom and which team does what. Will you appoint an individual who will serve as the primary contact for the external team and monitor their performance? Be clear about who is involved and how by stating it in the SLA.
- Plans if goals are unmet. You might not want to think about it, but your SLA should include formal consequences when a goal is unmet. These include a form of compensation from the service provider when they fail to meet agreed-upon goals. This can also come in the form of service credits.
- Conditions for cancellation. Under what conditions will the agreement be terminated? You realize you want to end the partnership when your goals are regularly unmet, or the current agreement no longer suits your needs. State the formal circumstances under which you might terminate the agreement to pursue a better one.
Outsourcing solutions will only grow in demand, considering the future of the BPO industry in this digital age. Thus, learning how to write an SLA for your BPO partnership is crucial.
An SLA enables you to hold your service provider accountable. You can also mitigate some of the risks by making your BPO partner compensate for your losses if agreed-upon needs are unmet. Conversely, outsourcing vendors prefer SLAs as they help them retain customers.
Mistakes to Avoid When Writing an SLA for Your Outsourcing Engagement
Businesses opt for outsourcing for many reasons, with cost savings being the most prevalent motivator. An airtight SLA is instrumental in achieving the desired outcomes of your outsourcing endeavors.
As you acquaint yourself with the art of crafting an SLA for your outsourcing engagements, it’s natural to encounter some missteps. However, by adhering to best practices, you can sidestep these five common mistakes that can hinder the creation of an effective SLA:
- Paying extra for better service. Assuming that paying more guarantees better service isn’t always the best strategy. Service providers often use a standardized technique to supply solutions, and it is frequently a matter of risk allocation rather than a clear correlation between cost and quality improvement.
- Expecting fines to save you money. Overloading the SLA with excessive “critical performance indicators” or metrics tied to financial penalties can diminish the relevance of crucial metrics, potentially impeding the overall effectiveness of the agreement.
- Being too vague. An SLA should encompass as many specific details as possible. It’s crucial to clearly define what aspects will be measured, the evaluation criteria for the engagement, and the precise exceptions and exemptions that apply.
- Raising the risk fee is too high. Setting the risk fee too high can result in an increase in the service provider’s pricing, as they may include the additional cost as a buffer against potential risks.
- New Content: Securing a professional edit for your agreement. After crafting the finer details of your SLA, ensure its clarity and professionalism by having it reviewed and edited by experts. This step can enhance the document’s precision and effectiveness, reinforcing your position in any outsourcing relationship.
The Bottom Line
SLAs form the core of service delivery reporting over the life of an outsourcing agreement. A poorly written SLA results in a report that does not match what is happening on the ground.
Writing an effective SLA is crucial to building and maintaining a successful BPO partnership. By following SLA best practices, you can ensure that your agreement is well-defined, effective, and realistic.
If you are looking for a reliable BPO partner, let’s connect!





