IN THIS ARTICLE
Table of Contents
Increasing numbers of customers prefer communicating with brands using multiple channels like email and live chat rather than phone calls. This holds for customer support too. Nobody likes waiting in a long call queue to talk to a customer service representative.
Contact centers let you connect with customers across various platforms. Contact centers register customer inquiries and resolve their problems using the customer’s preferred messaging channel.
This guide discusses contact center definitions, types, and use cases. It also briefly touches on Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS).
What Is a Contact Center?

A contact center is a central platform where companies handle all customer interactions across multiple channels. The primary aim of the contact center is to provide clients with efficient and effective sales assistance, customer service, and technical support.
Contact centers typically include two or more call centers but may also involve other customer service channels such as web chat, email, and social media interactions. Additionally, businesses often integrate their contact centers with customer relationship management techniques.
Contact centers are continuously growing in importance, with a $34.66 billion global market size in 2022. The increase in market size is due to customers’ changing expectations. Modern consumers expect brands to be consistently available across multiple channels, not just the phone.
Meanwhile, CCaaS is a cloud-based customer experience solution. This system or software helps companies with an omnichannel approach, allowing them to gain more insights into client needs and behavior. They can increase efficiency, refine service, and offer personalized customer experiences.
How Do Contact Centers Work?

Contact centers include representatives who manage omnichannel customer support, including chat, phone calls, email, and the web. Contact centers, by definition, are similar to call centers. However, contact centers communicate with customers using their preferred channel.
The important features of a contact center include:
- Automatic call distributor (ACD) systems, which allow contact center representatives to increase the number of tickets resolved while maintaining a good customer experience,
- Real-time reports enable contact centers to analyze and observe customer satisfaction and staff performance across the channels used.
- Scripts agents use this as a guide to provide customers with effective support and generate more sales.
- Contact databases store the customer information and interaction history that companies collect. This makes having the right context for conversations easier.
- Call recording so managers can monitor agent performance and customer satisfaction. It gives a reference for solving complaints or disputes.
- Interchangeable assignments that let reps share objects and contacts and collaborate while maintaining individual cubicles.
The Difference Between a Contact Center and a Call Center
Contact centers can be in-house or outsourced to a third-party service provider, like call centers. But how is a contact center different from a call center?
Let’s find out!
| Call Center | Contact Center |
|---|---|
| Call centers use a single-channel approach to customer support. They only manage inbound and outbound customer phone calls. | Contact centers use a unified or omnichannel communication approach to customer service. It includes messaging platforms other than calls, such as social media, live chat, email, and more. |
| Call center representatives have limited customer information since they utilize speech analysis software to analyze calls and gain journey insights. | Contact centers use artificial intelligence solutions and analyze multiple communication platforms. Hence, they have more personalized data and better profiling. |
| Call centers have limited customer self-service options. They use tools like interactive voice response (IVR), which help in routing calls to the appropriate agent. | Contact centers have more advanced customer self-support options that go beyond IVR. This includes FAQ web pages, an online knowledge base, chatbots, etc. These self-service options help buyers find information independently. |
Different Types of Contact Centers and Their Use Cases
Now that you know the contact center, it’s time to discover its types and use cases. The different types of contact centers include cloud-based, hardware, virtual, and hosted. Different contact centers have varying features and capacities.
Companies must decide which type of contact center is appropriate for their needs. Suppose your customer service representatives primarily answer incoming calls. You may not need omnichannel support. Conversely, invest in a product that can manage high volumes of customer tickets across channels if you want to support clients using multiple platforms.
Here’s a closer look at the different contact center models.
Hardware Contact Center
Companies can set up hardware contact centers by installing and managing servers onsite. This approach necessitates robust disaster recovery plans, sufficient space and capacity for server housing and maintenance, and a thorough process for hardware updates.
Legacy on-premises centers rely on hardware hosted on company servers, placing the responsibility of managing hardware, software, and infrastructure, including upgrades and maintenance, on the internal IT team.
A key advantage of this model is enhanced data security, as all information is stored on the company’s servers. This often translates to more reliable services, reduced call lag, and improved customer service quality.
However, the primary downside is the significant cost associated with maintenance and upgrades and the need for dedicated IT resources. Deploying an on-premise contact center is a time-consuming, labor-intensive process that demands substantial resources.
Cloud-based Contact Center
The internet server of the cloud provider hosts this type of contact center. An example of this is CCaaS.
Cloud-based contact centers allow businesses to handle all incoming and outgoing customer interactions online. Representatives can access the system anywhere using the internet. As such, the only things needed to access the software are a strong internet connection and sufficient bandwidth.
It also makes adding various channels easier, which is crucial when running omnichannel customer service.
There are several benefits to running a cloud contact center:
- It involves little to no routine maintenance or upgrades because the service provider manages the upkeep.
- It lets you access the software from anywhere with a reliable internet connection, making it easy for remote staff to use.
- The implementation is often faster since you don’t have to buy the hardware or software.
There are also downsides to cloud-based contact centers. It involves ongoing monthly or annual subscription fees, even though there are fewer upgrade and maintenance costs. This model is not ideal for businesses that would rather pay an upfront amount and don’t want to pay periodically to renew the software license.
Lastly, cloud-based contact centers may not be as customizable as onsite deployments. Cloud solutions may not be the best option for companies that require high-level customization.
Hosted Contact Center
For this model, the company outsources the infrastructure to an outside service provider that maintains the system externally. With hosted contact centers, the service provider keeps the server on their premises or in the cloud. This approach reduces upfront costs and maintenance, yielding a better investment return.
Companies often interchange “hosting services” and “cloud services.” However, cloud solutions are a subset of hosted services. Remember that hosted services include a solution outside the user’s physical location, which may be in the vendor’s premises or the cloud.
A hosted contact center has several benefits:
- A hosted contact center is feature-rich, so managers can easily add and implement features.
- It includes powerful integrations for centralized access to data.
- It has an advanced interactive voice response (IVR) system and call treatment.
- It is scalable and lean. There’s no on-premises hardware required.
- It provides detailed reporting.
Virtual Contact Center
These contact centers allow agents to work remotely from various locations. Staff could work from home or in an office space from anywhere globally. Meanwhile, virtual contact center software connects agents to their colleagues and customers.
Virtual centers have many upsides. They decrease overhead costs and provide customer support in various time zones. The focus is on matching the customer with the right agent at the right time.
Staff turnover is a major problem for legacy contact centers. And about 87% of agents report high stress levels due to the nature of tasks and working hours.
Virtual contact centers make it easier to deliver support 24/7 since agents work in different time zones. It also gives staff more flexibility, improving their job satisfaction. The result is round-the-clock support and a higher employee retention rate.
What Services Do Contact Centers Offer?

Knowing contact center definitions, types, and services is important in choosing the right customer service solution. The focus of a contact center is to fulfill client expectations with interactive and efficient customer service, technical support, and sales assistance through their chosen channel.
Here’s an overview of contact center services in detail:
Telephone Service
Contact centers are modern versions of traditional call centers. Handling large volumes of inbound and outbound calls is part of their primary service. Contact centers use an interactive voice response (IVR) system to manage incoming and outgoing calls. This technology uses voice commands or keypad entries to give information without human intervention.
Voice calls remain a relevant customer service channel; more than half of consumers across all age groups use the phone to contact an agent, according to Zendesk.
Contact centers manage two different types of calls:
- Inbound Calls. Inbound calls are incoming tickets from customers. For instance, a customer may have a question about connecting a recently bought device from your brand. You will receive an incoming call from that client asking for help in setting up.
- Outbound Calls. A contact center agent is the one making these calls. Outbound calls may be part of lead generation strategies, surveys, or direct sales. For instance, a health insurance provider may contact possible leads, explaining their insurance plans and converting them into paying clients.
Text Messaging Service
Transferred calls, long wait times, and language barriers are common customer complaints about voice support. In such cases, text messaging goes a long way toward improving experience and satisfaction.
Telephone calls and SMS let businesses effectively manage inbound and outbound customer communication. Text messaging services are fast, safe, and personal, and enhance employee productivity since they can interact with multiple customers simultaneously.
Companies can use text support to
- Send proactive updates regarding the customer’s problems
- Take feedback about the customer service
- Conduct various surveys
- Spark a two-way conversation
Chat Service
Chat is a popular communication channel due to its ease of use and efficiency. Most chat services have a high first contact resolution (FCR) rate, which measures the contact center’s ability to resolve issues on the first contact.
Customers can initiate interaction using a specialized chat window on your website. The chat box connects them to a bot or a live agent to help solve their issues.
There are two main types of chat services that contact centers offer:
- Chatbot. Chatbots use artificial intelligence (AI) to interact with customers, obtain relevant data about a problem, and even answer simple questions with human intervention. The bot can escalate the ticket to the next-best agent if problems require human assistance.
- Live chat. Live chat is a modern tool that most contact centers use. This differs from chatbots because a live agent answers questions and closes tickets at the other end. Live chat eliminates the need for IVR, lowers waiting time, improves first contact resolution, and works on the client’s shared screen in real time.
Social Media Service
Some contact centers provide social media services for digital platforms like WhatsApp, Twitter, and Facebook.
Businesses can use social media platforms to identify, analyze, and engage with clients daily. Companies can publish and track relevant content that boosts customer satisfaction using social media services.
Email Service
Email is another common digital customer service channel. Most contact centers use email management software to organize emails, letting agents compose and reply to large volumes of emails effectively.
Moreover, email management software provides templates as a guide when agents respond to customers. This lets contact center agents reply promptly, deliver standardized customer care, and improve satisfaction.
Advantages of Contact Center Services
Today’s customers want a personalized experience and prefer support beyond the one-platform approach. Thus, contact centers are increasing in popularity.
Let’s discuss the primary advantages of using a contact center service for your company.
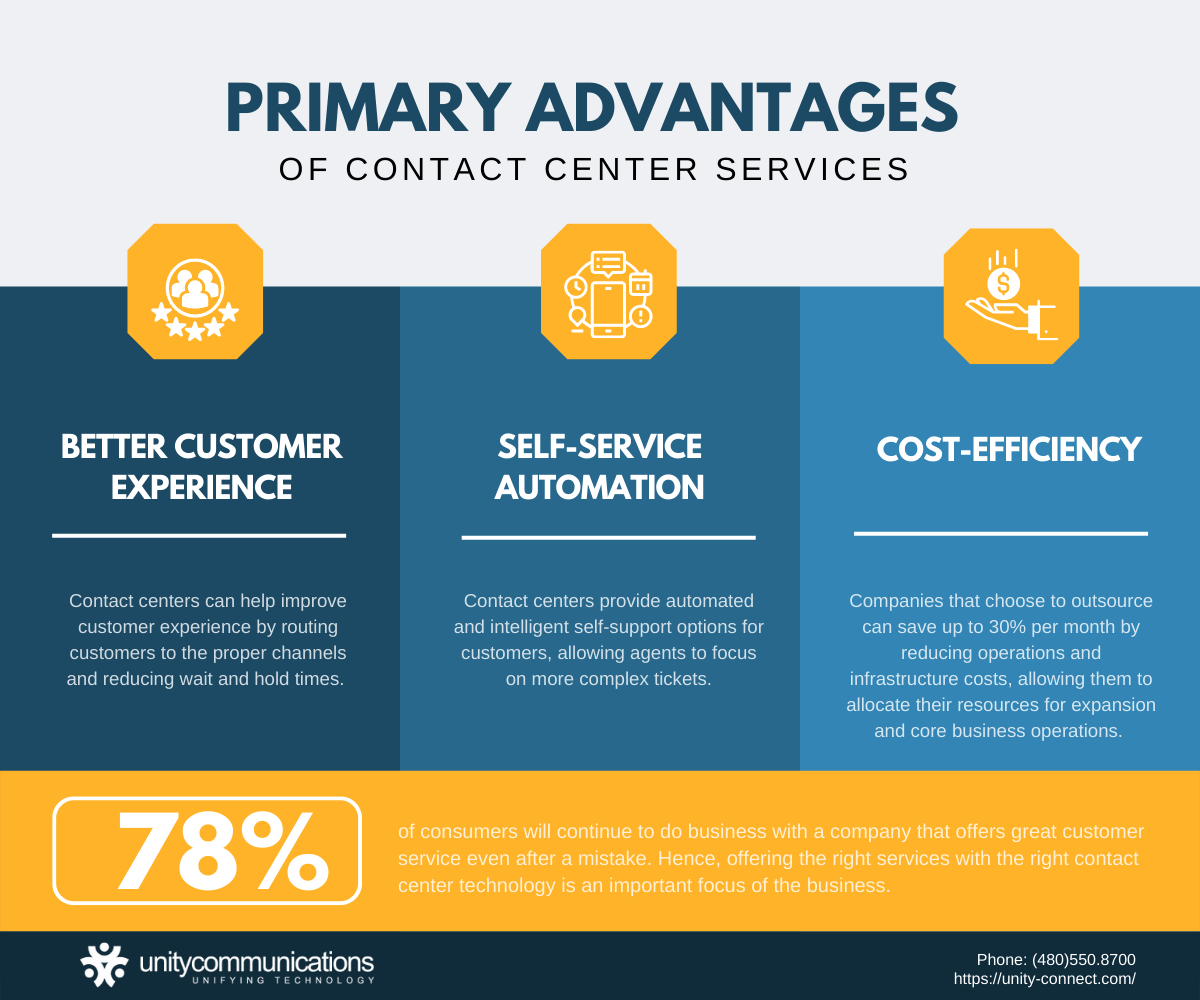
Better Customer Experience
Your contact center serves as the primary line of communication between your brand and customers. Hence, the quality of your customer service directly influences your business. Salesforce reports that 78% of consumers will continue to do business with a company that offers great customer service even after a mistake.
Use your contact center to provide an excellent customer experience. Contact centers connect customers to the best agent to solve their problems faster, increasing loyalty.
Self-service Automation
Customers expect a seamless self-service experience. Nothing is worse than being stuck in an endless customer self-service loop.
Contact centers provide automated and intelligent self-support options for customers, allowing agents to focus on more complex tickets. Contact center solutions empower customers to acquire the necessary information using touch-tone automated systems and natural language processing options to speak to an agent.
Cost-efficiency
A Harvard Business Review report shows that companies that choose to outsource can save up to 30% per month.
Since outsourcing companies need not hire new in-house agents, they can retain more resources to expand operations and advance areas. Similarly, companies no longer need to pay for infrastructure maintenance.
The Bottom Line
The insights provided offer a comprehensive understanding of contact center definitions, technologies, and services. A contact center is a central point for managing customer service across various platforms like web chat, email, social media, and voice calls. It empowers agents to have a holistic view of each customer’s interactions, enabling them to resolve issues efficiently without unnecessary repetition or delays for customers.
In today’s market, the quality of contact center services can significantly impact a business’s success. Companies delivering high-quality customer service enjoy greater loyalty and increased client engagement.
Therefore, leveraging the appropriate contact center technology to provide optimal services is crucial for any business strategy. For expert assistance in optimizing your contact center capabilities, contact Unity Communications.





